ESR or erythrocyte sedimentation rate is a blood test that can predict if there is any inflammation in the body. Inflammation in the body takes place as a response from the immune system against injury, infection, and several...
Introduction
ESR or erythrocyte sedimentation rate is a blood test that can predict if there is any inflammation in the body. Inflammation in the body takes place as a response from the immune system against injury, infection, and several other types of diseases, such as immune system disorders, certain cancers, and blood disorders.
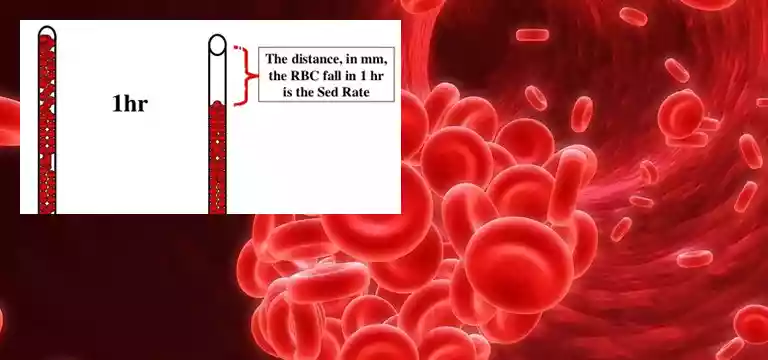
The function of the red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, is to carry oxygen throughout the body. To conduct an ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) test, a small amount of our blood is collected and sent to a laboratory for analysis. The laboratory technician takes the blood sample and carefully places it in a slim, tall test tube. The speed at which the red blood cells settle or descend to the bottom of the tube is then measured.
When the condition is normal red blood cells have a slow sinking rate. But, when there is inflammation present in the body, the red blood cells will tend to clump together. These clumps become heavier than individual cells, and they sink faster in the test tube. By observing the rate at which the red blood cells settle, doctors get to know the presence and severity of inflammation.
So, when the red blood cells sink at a faster rate in an ESR test it may indicate the patient has a medical condition causing the inflammation. The speed of sinking in the test result tells about how much inflammation a patient has. Faster ESR rates indicate higher levels of inflammation. However, an ESR test alone is not adequate to diagnose all the conditions leading to inflammation.
There are other names for ESR, such as the SED rate sedimentation rate, Westergren sedimentation rate, etc.
Why is the ESR test conducted?
An ESR test has to be combined with other modalities to help in diagnosing conditions that cause inflammation.
It can also be used to help monitor these conditions. There is a host of diseases that can cause inflammation, such as arthritis, infection, vasculitis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Additionally, an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) can be utilized to keep track of the progress of an ongoing condition.
The ESR test, when combined with other diagnostic tests, can immensely help in identifying and monitoring conditions associated with inflammation. The main objective of an ESR test is to help in diagnosing various inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, vasculitis, infections, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Who should get an ESR test done?
A doctor would order an ESR when a patient has signs and symptoms of any disease that causes inflammation. The symptoms may be specific to the condition the patient may have, but some common symptoms may include:
- Headaches
- Weight loss
- Inexplicable fever
- Joint stiffness
- Loss of appetite
- Neck or shoulder pain
- Anemia
The procedure
The ESR is a simple and basic blood test and the patient doesn’t have to make any special arrangements or get ready.
It is just that a patient should inform the consulting doctor before the test about every detail regarding the current medicines (and supplements) he or she is taking. Certain medications jeopardize the test results. It is also imperative to apprise the doctor about pregnancy, or if one is having periods during that time.
For the test, a healthcare technician or a nurse will draw a sample of the patient’s blood, usually from a vein in the arm. A band will be tied to the arm of the patient first so that the vein gets filled with blood and swell up. The nurse or technician will then clean up the area with antiseptic. Placing a needle into the vein they will collect the blood and transfer it to a vial or tube. It is hardly a two-minute process; thereafter the patient will be given gauze and a bandage over the area to stop the bleeding.
It is a safe and harmless blood test and the patient may just feel a slight sting as the blood is drawn, with a small bruise later on. There might be some dizziness and soreness along with some bleeding. These are all normal and nothing to be wary of.
Analysis of the results
After the blood sample is drawn from the patient and collected into a tube or vial, it is sent to a testing lab for examination. The results are usually out in one or two hours.
During the analysis, a lab technician will carefully transfer the red blood cells into a slim, elongated tube and observe their fall in one hour. When there is inflammation within the body, certain abnormal proteins in the blood will cause the RBC to aggregate and form clumps. These clumps, being heavier than individual blood cells, will fall at a much faster rate to the bottom of the tube compared to the single blood cells. This helps in identifying the presence of inflammation and its impact on the behavior of red blood cells.
The degree of inflammation will be proportionate to the rate of sinking of the red blood cells.
The doctor will analyze and use the results of the ESR test clubbing with the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and other test outcomes to make a diagnosis. An ESR test alone is not enough to diagnose conditions that cause inflammation.
A high ESR test result may be an indication that the inflation is caused by diseases like:
- Arthritis
- Systemic vasculitis
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Polymyalgia rheumatica
- Infection
- Kidney disease
- Rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases
- Heart disease
- Certain cancers
When the ESR test result is low it means the red blood cells sank more slowly than normal. This is due to diseases such as:
A blood disorder like polycythemia, sickle cell disease (SCD), Leukocytosis, a very high white blood cell count (WBC), heart failure, certain kidney and liver problems, etc
Conclusion
So, we now know that an ESR test is done for helping the doctor to diagnose if there is an inflammation in the body, where it is, and the underlying reason for it. Furthermore, an ESR test can also help in monitoring an existing inflammatory condition.
However, if the ESR results are not normal, it doesn't always translate into having a medical condition that calls for treatment. Pregnancy, a menstrual cycle, aging, obesity, drinking alcohol regularly, and exercise can also adversely affect ESR results. Taking certain drugs and supplements may also have a bearing on the results. That is why it is important to inform the doctor about any current medicines or supplements one is taking. It will help the doctor to make a proper and accurate diagnosis.
FAQs
Why does ESR increase?
ESR levels can be slightly higher due to errors in the laboratories, pregnancy, menstruation, or old age. The ESR result may predict inflammation in the body, but this test in itself is not specific to a particular disease process. It has to be clubbed with other techniques to diagnose an underlying condition.
What is a normal ESR level?
To be a normal ESR level it is less than 15 mm/hr for men under 50 years old. It should be less than 20 mm/hr for men over 50 years old. In women under 50 years old, it has to be less than 20 mm/hr. For women over 50 years old, it has to be less than 30 mm/hr.
Is ESR 40 high?
Yes, it is considered high. An ESR level of 40 mm/hr is a clear indication of a state of systemic inflammation among people who already have a confirmed inflammatory disease. Hence, it is imperative to examine whether the increase in ESR was accompanied by disease flares.
How can I reduce my ESR?
There are ways to lower inflammation and ESR. This can be achieved by regularly engaging in exercise, adopting a healthy and hygienic lifestyle, losing weight, and eating a nutritious balanced diet. It is important to note that a low sedimentation rate is often normal. In some cases, it may indicate blood cell disorders.
Which infection causes high ESR?
Certain conditions lead to a significantly high ESR level. They are:
- Autoimmune conditions (Rheumatoid Arthritis, Lupus, etc.)
- Kidney and/or thyroid diseases
- Infections
- Tissue injury and/or trauma
- Some classes of cancer
- Anaemia
Should I worry if my ESR is high?
If an ESR test shows that a patient’s red blood cells sink faster than normal, it could be that they have a medical condition leading to inflammation. The speed of the test result is an indication of how much inflammation they have. Faster ESR rates can be proportional to higher levels of inflammation.
What happens if ESR increases?
If someone has a condition that triggers inflammation or cell damage, the red blood cells tend to clump together. As a result, they become heavier and settle faster. The faster the red blood cells settle and fall, the higher the ESR.
Is ESR high due to urine infection?
If results are positive for CRP, WBC, and ESR, it may indicate upper urinary tract infection including acute pyelitis or pyelonephritis (APN).









