Are you planning a nuclear medicine procedure? If so, and if you're looking for an easy-to-understand guide to the process, you've come to the right place.
We've compiled everything you need to know about nuclear medicine in this article, including information on what it is, how it works, and how it is delivered.
What is nuclear medicine?
Nuclear medicine uses radioactive compounds to diagnose and treat diseases. A nuclear medicine physician administers a radioactive compound called a radiotracer that travels throughout your body emitting radiation as it goes. Unique cameras detect the radioactivity emanating from your body and create images that help the physician diagnose your condition. Afterward, the radioactive compounds exit your body through your urine or feces and can be tracked using special equipment.
The images created by these procedures are called radiopharmaceutical images. They are distinct from x-ray images in that they show the distribution of substances in organs and tissues (not bones and muscles), making them more helpful in diagnosing diseases affecting those organs and tissues.
What tests are performed under Nuclear Medicine?
Many medical disorders and diseases are diagnosed using Nuclear Medicine Scans. The following are some of the more common Nuclear Medicine tests:
Kidney scans- These are used to assess and detect any abnormalities in the kidneys. The renal blood flow may be obstructed, or the function of the kidneys may be faulty.
Thyroid Scan- These are used to assess thyroid function or to assess a thyroid nodule or mass more thoroughly. Click here to know about procedure of Thyroid Scan Test.
Bone Scan- These are used to assess any degenerative or arthritic changes in the joints, detect bone illnesses and tumors, and pinpoint the source of bone discomfort or inflammation.
Gallium Scan- These are used to detect active infections and/or inflammatory illnesses, malignancies, and abscesses, among other things.
Heart scan- These are used to detect aberrant heart blood flow, estimate the extent of heart muscle damage following a heart attack, and/or measure heart function.
Brain Scan- These are utilized to look at issues with the brain and/or the brain's blood circulation.
The Three Procedure For Nuclear Medicine Test
There are several types of nuclear medicine scans: SPECT, PET, and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT/CT). The procedures for all three scans are similar:
1) An injection is made into a vein
2) The patient waits for the radioactive material to be absorbed by the target part of the body
3) A scan is taken while the patient lies down with no movement
4) The scan takes anywhere from 5 to 60 minutes, depending on what part of the body is being scanned
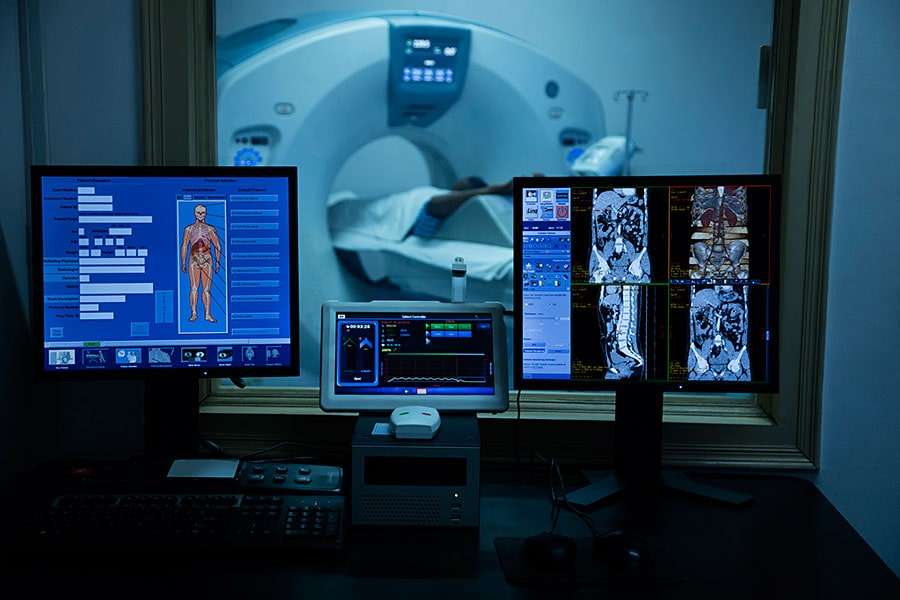
How does it work?
In order to begin a nuclear medicine scan, a patient is taken to a room where they are injected with radioisotopes. After the patient receives the injection, they will wait for the isotopes to give off radiation, which will be detected and recorded by a camera placed in the room.
This process can take anywhere from a few minutes to hours depending on the type of test you are getting. The amount of time it takes depends on how much radiation is necessary for the scan and how much radiation the patient's body can withstand without being harmed.
The camera collects all the emitted and reflected gamma rays, and the computer uses algorithms to create a 3-D representation of where the radioactive substance was injected into the body.
The images that are recorded by the camera are then sent to a computer program that calculates where the most concentrated areas of radiation are. These areas are used to determine what part of the body is emitting radiation and take images of it.
What you may experience during and after the Nuclear Medicine procedure?
The nuclear medicine scan itself is painless, although there are certain precautions that need to be taken prior to the scan.
#1 It typically takes about 30 minutes, depending on the tests being performed.
#2 You will lie still for the procedure, and some of your blood may also be drawn.
#3 Most of the time, you will stay in the hospital or a clinic for a few hours after the procedure to monitor you and ensure your safety.
#4 The procedure will not have any long-lasting side effects.
#5 Breathing and heart rate changes, especially when changing positions, are normal during the examination. Afterward, you can go home with no restrictions on diet or activities.
#6 If you experience any unusual symptoms after the exam, contact your healthcare provider right away.
#7 During the procedure, you may feel some warmth in your chest or neck area. Afterward, you should not feel any different than before the scan.
What are the limitations of General Nuclear Medicine?
General nuclear medicine is used to detect and diagnose a wide variety of conditions. It does this by using radioactive tracers, which are a bit like microscopic detective badges. When you get a nuclear medicine scan, the radioactive tracer goes to work looking for the source of your pain, disease, or issue.
The limitations of general nuclear medicine are that it can be expensive and time-consuming, and the results may not be as clear-cut as with other forms of imaging. Also, some tracers may have short half-lives (the amount of time they're effective for), so you may need to get more than one test during your appointment.
What does the future hold for General Nuclear Medicine?
What does the future hold for nuclear medicine? It's hard to say. In 2022, the nuclear medicine industry will be the same as it is now. The only difference will be the number of people who want to work in the nuclear medicine industry. The reason they want to work in this field will be because they are excited about the prospect of specializing in diagnosing and treating illnesses. Due to the large number of people who are interested in working with nuclear medicine, the supply of qualified doctors, physicists, and engineers will not be able to keep up with demand. Nuclear medicine will continue to be a well-respected field of study and career choice for many years to come.









