Varicella-zoster infection (VZV), moreover known as human herpesvirus 3 (HHV-3, HHV3) or Human alphaherpesvirus 3 (taxonomically), is one of nine known herpes diseases that can contaminate public. It causes chickenpox...
Varicella-zoster infection (VZV), moreover known as human herpesvirus 3 (HHV-3, HHV3) or Human alphaherpesvirus 3 (taxonomically), is one of nine known herpes diseases that can contaminate public. It causes chickenpox (varicella) commonly influencing children and youthful grown-ups, and shingles (herpes zoster) in grown-ups but seldom in children. VZV contaminations are species-specific to people. The infection can survive in outside situations for many hours.
The study of disease transmission
Essential varicella zoster infection disease comes about in chickenpox (varicella), which may result in complications counting encephalitis, pneumonia (either coordinate viral pneumonia or auxiliary bacterial pneumonia), or bronchitis (either viral bronchitis or auxiliary bacterial bronchitis). Indeed when clinical indications of chickenpox have settled, VZV remains torpid within the apprehensive framework of the tainted individual (infection idleness), within the trigeminal and dorsal root ganglia.VZV enters through the respiratory framework. Having an brooding period of 10–21 days, averaging at 14 days. Focusing on the skin and fringe nerve, the period of sickness is from 3 to 4 days. 1–2 days some time recently the hasty shows up is when this infection is the foremost infectious
Transmission
Varicella is exceedingly infectious. The infection can be dispersed from individual to individual by coordinate touch, inward breath of pressurised canned derivatives from vesicular liquid of skin injuries of intense varicella or zoster, and conceivably through contaminated respiratory emissions that moreover may be aerosolized. An individual with varicella is considered infectious starting one to two days some time recently with a hasty onset until all the chickenpox injuries have crusted. Inoculated individuals may create injuries that don't crust. These individuals are considered infectious until no unused injuries have shown up for 24 hours.
Signs and indications
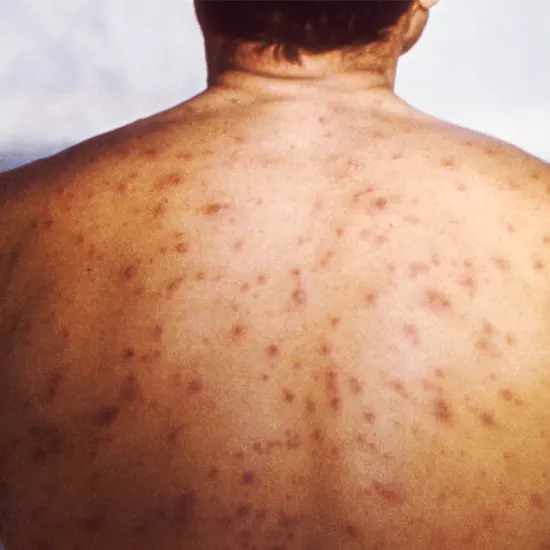
Chicken pox
In children, chicken pox shows with fever and fractiousness, followed by vesicular hasty emission. The hasty in the long run coverings and heals.
Chicken pox moreover can happen in grown-ups without characteristic or immunization initiated resistance to VZV.
Herpes zoster (shingles)
The foremost common introduction is the shingles vesicular hasty, which most commonly influences a thoracic dermatome. Torment and paresthesia regularly are the primary indications of VZV contamination. Until the characteristic vesicular hasty ejects, conclusion may be troublesome. A prodromal period amid which side effects may shift is common.
After a prodromal ailment of torment and paresthesias, erythematous macules and papules create and advance to vesicles.
The vesicles inevitably hull and resolve.
Torment and tactile misfortune are the normal side effects.
Engine shortcoming too may happen and as often as possible is missed on examination.
Zoster multiplex
Shingles may show up in numerous dermatomes, both touching and noncontiguous, on either side of the body.
Immunocompromised people are more helpless.
Wording depends on the number of included dermatomes and on whether the condition is one-sided or respective (eg, zoster duplex bilateralis alludes to the involvement of two one-sided dermatomes)
Cases of zoster at the same time occurring in seven noncontiguous dermatomes have been detailed
Zoster sine herpete
VZV contamination may reactivate without inducing cutaneous vesicles. These patients have serious dermatomal torment, conceivable engine shortcoming, and conceivable hypesthesia, but no obvious hasty or vesicles.
VZV infection may display as intense fringe facial palsy in 8-25% of patients who have no cutaneous vesicles. Typically more common in immunosuppressed patients who utilize acyclovir (or other operators) as zoster prophylaxis
Ramsay-Hunt disorder
This disorder happens when the geniculate ganglion is included. The clinical introduction incorporates the taking after:
- A fringe facial paralysis
- Torment within the ear and face
- Vesicles within the outside ear canal (not continuously present)
- Extra sound-related and vestibular side effects in a few cases
- Keratitis (herpes ophthalmicus)
Herpes ophthalmicus is induced by reactivation of VZV infection within the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve.
The introduction may include conjunctivitis or corneal ulcers.
Complications incorporate visual deficiency.
Vesicles don't have to be displayed.
Seldom, the infection moves along the intracranial branches of the trigeminal nerve, causing thrombotic cerebrovasculopathy with extreme migraine and hemiplegia.
Determination
Determination of chicken pox or herpes Zoster is regularly clinical.
On the off chance that in question research facility tests can be performed. PCR to distinguish VZV DNA is the foremost dependable and delicate strategy. Coordinate immunofluorescence (DFA) to distinguish VZV antigen is the moment choice; affectability is as it were 60–70% of cases are perceptible by PCR. Other strategies can be utilized to affirm VZV contamination that are less ideal and less commonly utilized. Viral culture of VZV is conceivable but is harsh, time-consuming, and costly since it requires extraordinary media.
In cases of acyclovir-resistant VZV, discoveries of transformations in thymidine kinase can be decided by PCR and sequence analysis.
MRI may be valuable on the off chance that myelitis, meningitis, or encephalitis is suspected.
Lumbar puncture may be accommodating on the off chance that signs recommend myelitis, meningitis, or encephalitis.
Treatment of Chickenpox
Symptomatic treatment
In some cases verbal antiviral specialists
IV acyclovir for immunocompromised patients and others at hazard of serious illness
Gentle cases of chickenpox in children require symptomatic treatment. Alleviation of tingling and avoidance of scratching, which inclines to auxiliary bacterial contamination, may be difficult. Wet compresses or, for serious tingling, systemic antihistamines and colloidal cereal showers may offer assistance.
Cleaning agents ought to not be connected unless lesions become contaminated; bacterial superinfection is treated with antibiotics.
Patients ought to not return to school or work until the ultimate injuries have crusted.
Antivirals and chickenpox
Verbal antivirals, when given to immunocompetent patients inside 24 hours of the rash's onset, marginally diminish indication term and seriousness. Be that as it may, since the infection is by and large generous in children, antiviral treatment isn't routinely recommended.
Verbal valacyclovir, famciclovir, or acyclovir ought to be given to solid individuals at hazard of moderate to serious illness, including patients
12 a long time of age or more seasoned (18 a long time of age or more seasoned for famciclovir)
With skin clutters (especially skin inflammation)
With unremitting lung infection
Getting long term salicylate treatment
Getting corticosteroids
The dose is famciclovir 500 mg 3 times a day or valacyclovir 1 g 3 times a day for grown-ups. Acyclovir could be a less alluring choice since it has poorer verbal bioavailability, but it can be given at 20 mg/kg 4 times a day for 5 days for children ≥ 2 years and ≤ 40 kg. The measurements for children > 40 kg and grown-ups is 800 mg 4 times a day for 5 days.
Prognosis for Chickenpox
Chickenpox in children is once in a while extreme. The serious or deadly malady is more likely the taking after:
- Grown-ups
- Patients with discouraged T-cell resistance (eg, lymphoreticular cancer)
- Those accepting corticosteroids or chemotherapy or who are something else immunosuppressed
- Patients being treated with tumor rot figure (TNF) antagonists









