
Tuberculosis caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis that usually attacks the lungs. But it can also involve other body parts like- Kidney, spine, lymph nodes and brain.
Tuberculosis is a bacterial lung disease, which can be transferred from one person to another.
According to WHO, TB is the 13th leading cause of death, while it is the second most common infectious disease after covid-19. In India it is reported that every 6th death in one Lakhs population is due to Tuberculosis. The government of India also reported that Delhi has the highest TB incidence rate in India.
Tuberculosis horror has continued till now since the 20th century all over the world. In early 1904 it was known as “Great white Plague” because of the paleness of patients.
Let’s understand- What it is, Why it occurs, How can we know that we are suffering from TB and finally How to prevent and cure?
What is Tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis that usually attacks the lungs. But it can also involve other body parts like- Kidney, spine, lymph nodes and brain.
TB is mainly spread through person to person from infected air droplets which are aerosolized by coughing, sneezing or speaking.
Risk of developing tuberculosis depends on an individual immune system. There is a difference between being infected with TB bacteria and active tuberculosis disease.
Stages of Tuberculosis
Exposure
The interaction of tuberculosis bacteria with humans occurs with the inhalation of infected aerosol from a person who has TB.
In this stage the person shows no signs and symptoms, negative skin test, and a normal chest X-ray.
Latent TB infection
This is the stage when a person has TB bacteria in their body but no signs and symptoms of the disease. A TB bacterium lives in an individual body in an inactive phase throughout life.
In this stage a person will show positive Skin test or blood test but normal Chest X-Ray.
There are no signs of active infection in the body but this person is a carrier of Tuberculosis bacteria.
Infectious stage
In this stage a person develops signs and symptoms. This person could have a positive or negative skin test or blood test, positive chest x-ray, biopsy or other finding showing an active infection.
Who Can Develop Tuberculosis Diseases?
Following people are at higher risk
- People in close contact with TB infected person
- Person with poor immune system
- More common in low income people
- Alcoholics
- Person with systemic disease like – diabetes, HIV and cancer
- A person taking medication to suppress the immune system or under chemotherapy
- Drug abusers
What Are the Symptoms of TB?
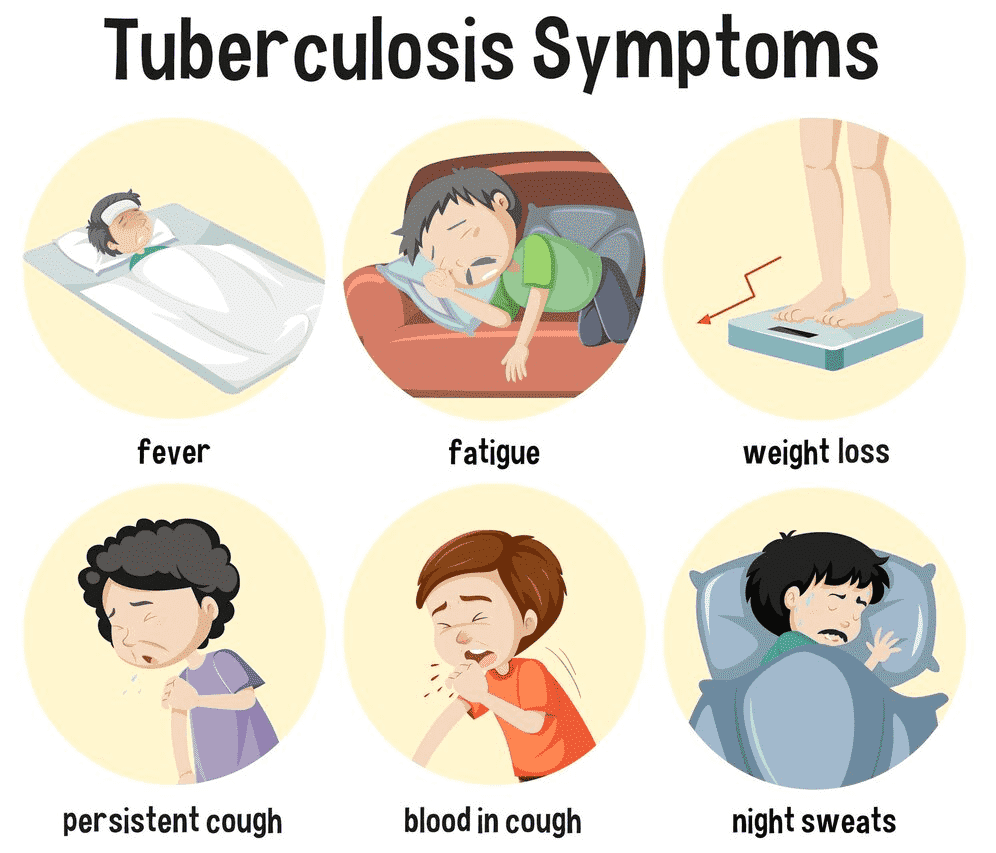
TB is classified as pulmonary tuberculosis, extra pulmonary tuberculosis and both.
Most common symptoms are
- Chills or fever
- Night sweats
- Prolonged cough more than 3 weeks
- Chest pain
- Weakness/Fatigue
- Sudden loss of weight
- Poor growth in children
- Coughing sputum or blood
- Breathlessness
- Back pain
Extra pulmonary TB (TB outside the lungs), most common sites are
- Tuberculous Lymphadenitis Lymph node TB presents as painless swelling of the lymph nodes.
- Pleural TB/ Tuberculous pleural effusion
Pleural TB is usually presented with pleural effusion caused by the immune response of an individual.
Second most common extrapulmonary tuberculosis
This can be diagnosed with the help of laboratory tests and radiology tests. Other than this patient needs a HIV test, pleural aspiration or pleural fluid is taken for cytology, pleural fluid/serum protein, serum LDH, interferon-gamma either by ELISA and radioimmunoassay(RIA) and ADA level. In few patients with uncertainty in diagnosis, pleural biopsy is advised it can be closed or thoracoscopic.
- TB of upper airways
- Genitourinary TB
- Skeletal TB
- Tuberculous Meningitis
- Gastrointestinal TB
- Pericardial TB
- Millary TB
- Disseminated TB
- Tuberculous otitis- TB bacteria affecting the ear and it may cause hearing loss, ear drainage and tympanic membrane perforation.
- TB Nasopharynx
- Adrenal TB
- Oral TB- it may occur at any location of the oral mucosa. Tongue is most commonly involved. Other sites include – Salivary gland, gingival, uvula, Palatine tonsil and floor of the mouth. It may be in the form TB Osteomyelitis.
- Oral lesions may appear as ulcers, nodules, tuberculomas and periapical granulomas.
- Congenital TB- Transplacental spread of bacteria to fetus or from ingestion of amniotic fluid of affected mother
How Is Tuberculosis (TB) Diagnosed?
It can be diagnosed with a suspected case through history and physical examination and diagnostic tests.
Diagnostic tests to evaluate the TB
- Tuberculin test
- AFB test
- Culture Mycobacterium Atypical Non-Tuberculous Mycobacterium-NTM
- X-ray chest
- Ultrasound
- CT
- Note:- In certain cases with uncertain diagnoses, suspected malignancy and in HIV positive who are at higher risk of disseminated TB
- Most commonly advised in case Chest, axillary tuberculous lymphadenitis and extra pulmonary tuberculosis.
- HRCT
- CECT
- MRI
- To confirm the involvement and extent MRI is an important tool for confirmation. For Ex- In case of lymphadenitis MRI Neck is advised.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for tuberculosis
- Histopathologic examination
- Ancillary diagnostic tests
- HAINS Mycobacterium Tuberculosis First & Second Line Drug Resistance Profile
- Smear Test - Sample is obtained from the draining sinus or FNA. Ziehl-Neelsen staining of the smears may reveal mycobacteria in the fresh specimens.
- Mantoux test
- FNAC
- Biopsy
Treatment of TB (Tuberculosis)
Treatment depends on the latent or active TB.
Pharmacological
First line of Drug
- Isoniazid.
- Rifampin (Rimactane).
- Rifabutin (Mycobutin).
- Rifapentine (Priftin).
- Pyrazinamide.
- Ethambutol (Myambutol).
Second line of drug
- Bedaquiline
- Linezolid
- Moxifloxacin
- Levofloxacin
- Clofazimine
- Cycloserine (Cs)
- Para-aminosalicylic acid
Antitubercular chemotherapy - Aim of anti-tubercular therapy are:
- Kill dividing bacteria
- Kill persisting bacilli
- Prevent emergence of resistance
Non-pharmacological Management
It includes preventive measures and providing education to common people.
Tuberculosis Vaccination
BCG – Bacilli Calmette-Guerin vaccine is used against Tuberculosis. BCG vaccine is an injection given to children that helps in developing the immune system that fights against TB.
Tuberculosis is a highly infectious disease and BCG Vaccine works as an immune booster and helps an individual from getting serious TB.
Best time for getting a TB vaccine is within a few days of kids born and till 6 months, or they can be vaccinated till 5 years at any time.
TB is one of the most common diseases in India. Early diagnosis is the crucial element for recovery. Tuberculosis bacteria remain in the latent state in an individual with no sign and symptoms but individual as a carrier because bacteria are living inside the body.
Do early diagnosis and validation from tuberculosis test facilities the doctor for preventive TB treatment at the time of infection level.
Tips From Ganesh Diagnostic and Imaging Center
- Follow good cough hygiene
- Safe use of injections.
- Good ventilation in patient room as TB can remain suspended in the air for several hours with no ventilation
- Natural Light- UV light kill TB bacteria
- Regular monitoring via health checkup packages
- Infected patient should be isolated
- Early diagnosis with us with heavy discount on TB test
Why Should Ganesh Diagnostic and Imaging Centre Be Your Choice for Your Health?
Ganesh Diagnostic offers a wide range of diagnostic services and can meet all of your diagnostic requirements, including radiological and pathological examinations. We are equipped with high-quality services and various fully automated advanced machines to ensure accurate reports at an affordable price.
Ganesh Diagnostics are accredited with NABH & NABL Certified for accessibility we provide Free Home Sample collection Service and Free Ambulance service to our valuable customers.
We offer many health examinations at our centre that demonstrate safety, prudence, and care.
Here at Ganesh Diagnostic and Imaging Centre, we offer straightforward and comprehensive health packages for any tests to guarantee the prompt prescription of therapy to protect your health.
We care for you
For any query contact us 24X7









