Opisthorchiasis could be a parasitic malady caused by certain species of the sort Opisthorchis (particularly, Opisthorchis viverrini and Opisthorchis felineus). Incessant disease may lead to cholangiocarcinoma, a cancer of the...
Opisthorchiasis could be a parasitic malady caused by certain species of the sort Opisthorchis (particularly, Opisthorchis viverrini and Opisthorchis felineus). Incessant disease may lead to cholangiocarcinoma, a cancer of the bile channels.
Medical care and loss of wages caused by Opisthorchis viverrini in Laos and in Thailand costs around $120 million annually.In Asia, contamination by Opisthorchis viverrini and other liver flukes influences the poorest people.Along with other foodborne trematode diseases such as clonorchiasis, fascioliasis and paragonimiasis, opisthorchiasis is recorded among the World Wellbeing Organization's list of dismissed tropical maladies.
Opisthorchiasis Pathophysiology
Opisthorchiasis may be a parasitic contamination caused by the liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini, which is endemic in a few parts of Southeast Asia, especially in Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, and Cambodia. The life cycle of the parasite includes two middle has, freshwater snails and angle, and the authoritative have, which is more often than not a human or a warm blooded creature that bolsters on crude or undercooked contaminated angle.
The pathophysiology of opisthorchiasis involves several instruments, counting mechanical obstacle, irritation, fibrosis, and carcinogenesis. The grown-up flukes live within the bile channels of the liver and can cause mechanical hindrance of the bile conduits, driving to cholangitis, cholecystitis, and biliary cirrhosis. The obstacle can moreover cause a reinforcement of bile, driving to jaundice and pruritus.
In expansion, the flukes discharge antigens and eggs that trigger an provocative reaction, which can lead to harm to the bile conduits and liver tissue. The persistent irritation can too lead to fibrosis CBC Blood and scarring of the liver tissue, which can advance to cirrhosis and entrance hypertension. The entry hypertension can cause complications such as variceal dying, ascites, and hepatic encephalopathy.
Besides, the incessant aggravation and fibrosis can moreover lead to the improvement of cholangiocarcinoma, a malignant tumor of the bile channels. Opisthorchiasis is considered a major hazard figure for cholangiocarcinoma, and the rate of this cancer is essentially higher in ranges where the disease is endemic.
In general, opisthorchiasis can cause a run of clinical appearances, counting stomach torment, jaundice, pruritus, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, and dietary insufficiencies. The seriousness of the side effects depends on the term and escalation of the contamination and the host's safe reaction. The conclusion is more often than not made by distinguishing the eggs in the stool or by imaging considerations such as ultrasound or CT check. Treatment includes antiparasitic medicine such as praziquantel and steady care for the complications.
Signs and side effects
Side effects of opisthorchiasis/clonorchiasis
Indications of opisthorchiasis are undefined from clonorchiasis. Around 80% of tainted individuals have no indications, in spite of the fact that they can have eosinophilia. Asymptomatic disease can happen when there are less than 1000 eggs in one gram of feces. Contamination Chest X-Ray is considered overwhelming when there are 10,000-30,000 eggs in one gram of feces. Side effects of heavier diseases may incorporate the runs, epigastric and right upper quadrant torment, need of craving, weariness, yellowing of the eyes and skin and mellow fever.
These parasites are long-lived and cause overwhelming unremitting contaminations which will lead to collection of liquid within the legs (edema) and within the peritoneal depression (ascites),enlarged non-functional gallbladder conjointly climbing cholangitis, which can lead to periductal fibrosis, cholecystitis and cholelithiasis, obstructive jaundice, hepatomegaly and/or entry hypertension.
Causal Specialists
Trematodes (flukes) Opisthorchis viverrini (Southeast Asian liver fluke) and Opisthorchis felineus (cat liver fluke).
Life Cycle
The grown-up flukes store completely created eggs that are passed within the feces The number 1. After ingestion by a appropriate snail (to begin with middle of the road have) The number 2, the eggs discharge miracidia The number 2a , which experience within the snail a few formative stages (sporocysts The Immunoglobulins Blood number 2b, rediae The number 2c, cercariae The number 2d ). Cercariae are discharged from the snail The number 3 and enter freshwater angle (moment halfway host), encysting as metacercariae within the muscles or beneath the scales The number 4.
The mammalian conclusive have (cats, pooches, and different fish-eating warm blooded animals counting people) ended up tainted by ingesting undercooked fish containing metacercariae. After ingestion, the metacercariae excyst within the duodenum The number 5 and climb through the ampulla of Vater into the biliary channels, where they join and develop into grown-ups, which lay eggs after 3 to 4 weeks The number 6. The grown-up flukes (O. viverrini:
- 5 mm to 10 mm by 1 mm to 2 mm; O. felineus:
- 7 mm to 12 mm by 2 mm to 3 mm) dwell within the biliary and pancreatic ducts of the mammalian have, where they join to the mucosa.
Introduction
Most contaminations are asymptomatic. Gentle diseases may cause dyspepsia, stomach torment, loose bowels or obstruction. Longer-term infections may cause more serious indications and may lead to hepatomegaly and ailing health. Cholangitis, cholecystitis, and cholangiocarcinoma may be created but only seldom.
Contaminations due to O. felineus may moreover display an intense stage comparable to Katayama fever (schistosomiasis), with fever, facial oedema, lymphadenopathy, arthralgias, hasty and eosinophilia. Persistent O. felineus contamination may moreover include the pancreatic ducts.
Differential conclusion
- Viral hepatitis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Fiery bowel infection.
- Leishmaniasis.
- Essential biliary cirrhosis.
- Tuberculosis.
- Typhoid.
- Carcinoma of head of pancreas.
- Cholangiocarcinoma.
Examinations
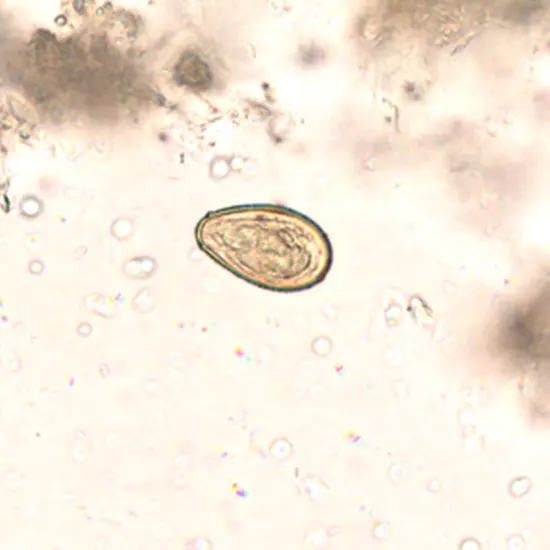
Microscopic stool examination may reveal the eggs. Duodenal goal is more touchy for this reason than examination of two stool specimens. An enzyme-linked immunosorbant assay (ELISA) strategy for recognizing antigen in the stool may be utilized to analyze opisthorchiasis. Polymerase chain response procedures are being created to move forward determination. FBC may uncover frailty and eosinophilia.
Administration
- Praziquantel is the treatment of choice. Albendazole is an elective.
- Intercurrent bacterial diseases are treated with suitable anti-microbials.
- Surgery may be needed to treat biliary tract complications.
Complications
- Frailty
- Intercurrent bacterial disease
- Pancreatitis
- Pyogenic cholangitis
- Cholangiocarcinoma
Guess
- Early, direct pervasions are likely to be cured without complications.
- Incessant or severe infestations tend to lead to complications, and passing isn't unprecedented.
Anticipation
Legitimate cooking of angle. Solidifying angle expecting for crude utilization. Utilize of molluscicides is the foremost visit open wellbeing intercession, as it avoids the transmission of numerous other trematodes, counting Schistosoma spp. Treatment of creatures to diminish the supply and stock misfortunes has been utilized. Prophylactic use of praziquantel.









