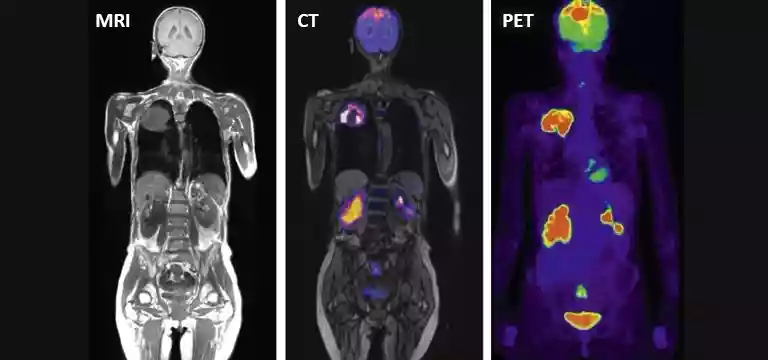
In the field of medical science, diagnostic imaging is integral to patient care and healing. Among various diagnostic techniques, medical imaging is a foremost modality helping doctors to detect and treat diseases...
In the field of medical science, diagnostic imaging is integral to patient care and healing. Among various diagnostic techniques, medical imaging is a foremost modality helping doctors to detect and treat diseases accordingly.
Medical imaging refers to the technique of visual representation of the patient’s body of the internal structures and the function of different organs and tissues. These images are indispensable for clinical purposes and for studying the normal or abnormal anatomy of the human body. The internal structures of the human body made available by imaging procedures reveal the internal structures beneath the skin and bones, which is the diagnosis doctors require to treat and heal patients.
Hence, there are several imaging modalities such as Computed tomography (CT), positron emission tomography (PET), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), etc., which are regarded as advanced diagnostic techniques.
These techniques, although have the same purpose of detecting internal anomalies in the patient’s physiology, have some basic differences in their approach, processes, and requirements. Before exploring “what is the difference between MRI, PET, and CT scans”, we need to know each of the imaging modalities first.
We’ll explore those similarities and dissimilarities of these imaging techniques in this article:
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scans
Magnetic resonance imaging or MRI is that medical imaging modality in radiology that provides pictures of the human anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scans are based on the principle of using strong magnetic fields, radio waves, and magnetic field gradients, to churn out images of the internal organs in the patient’s body.
This is painless and the procedure gets over in about 15 to 90 minutes. It depends on the area which is being examined and how many pictures are needed.
In some cases, MRI scans necessitate the use of a contrast agent or dye, which is needed to elicit clearer images of certain tissues and blood vessels. Some people may feel claustrophobic and hence they should divulge this to their doctors beforehand. The healthcare provider will prescribe a relaxant to the patient so that the shoe process becomes seamless. The patient will be in constant communication with the technician who sits in an adjacent room while conducting the scan.
Moreover, the patient needs to be still while inside the scanner so that the images do not become blurry.
PET (positron emission tomography) scans
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a medical imaging modality that is based on using a radioactive substance called radiotracers. The PET scan helps in seeing and measuring changes in metabolic processes along with other activities of the body such as the flow of blood, chemical composition of regions, and absorption.
The procedure of a PET scan
As mentioned above, a PET scan is done using a radioactive tracer, which is administered through a vein (IV). The needle is mostly inserted on the inside of the patient’s elbow. Once it is injected, the tracer traverses through the blood and accumulates in tissues and organs. As the tracer gathers, it helps the radiologist to visualize certain parts of the body more clearly.
The patient has to wait for at least one hour for the tracer to be absorbed by the body.
After that, the patient will lie down on an examination table that slides into the scanner, which looks like a large tunnel. These signals are then converted into 3D images by a computer. The images can be displayed on a monitor and from it the consulting doctor carefully reads and takes further decisions on the course of treatment.
The patient has to lie down very still during the scanning process. Any or too much movement can result in blurry images and may cause errors. The duration of the scan is dependent on what part is being scanned and how many pictures need to be captured for that.
The doctor might order a PET scan if he feels a need to visualize the body’s functioning regarding:
- Blood flow
- Oxygen use
- Metabolism of organs and tissue
As for side effects, there shouldn’t be any and the patient can leave for home the same day after the test. Usually, the test results of a PET scan are not available on the same day and those will be sent to the consulting doctor of the patient later.
Disadvantages of a PET scan
It is crucial to consider a few drawbacks of a PT scan. A PET scan is likely to dispense false results when there is an abnormality in chemical balances within the body. Specifically, if a patient is diabetic or if they have eaten anything a few hours before the scan, it can adversely affect the results due to an altered blood sugar or blood insulin level.
CT (computed tomography) scans
A computed tomography scan or CT is referred to as a medical imaging modality that provides detailed images of the internal parts of the human body. The CT scan is performed by radiographers or radiology technologists.
What can a CT scan diagnose?
CT scans are capable of producing detailed images of several internal structures within the body, such as blood vessels, internal organs, and bones. Hence, CT scans can diagnose a host of conditions like damage to bones, problems with blood flow, injuries to internal organs, stroke, and cancer.
During the CT scan procedure, the patient has to lie in a tunnel-shaped machine. The machine then rotates (the inside part rotates) and clicks a series of X-rays from separate angles. The clicked images are sent to a computer, to combine and create images of slices, or cross-sections, of the patient’s body.
So, why is a CT scan most commonly used? A CT scan is most commonly ordered in case of chronic back pain or injury to the spine. So, the doctor may order a CT scan to study the spinal fractures of the patient and assess the spine’s condition before and after invasive procedures like surgery.
Conclusion
PET/CT machines have a long history of usage in the healthcare domain compared to PET/MRI machines. The latter is also costlier than PET/CT machines.
Although it depends on the reasons whether a patient needs an MRI or not, the doctor might have other angles to opt for a PET/CT over a PET/MRI.
Most PET tests are conducted in a PET/CT combination machine. If someone needs both a PET and an MRI scan, they can be done together in the latest PET/MRI machines.
Patients who have metal or medical implants, tattoos, have claustrophobia, or could be pregnant, should notify their physician before going for an MRI, PET, or CT scan.
FAQs
Which is better CT scan or PET scan?
A CT scan is capable of providing intricate visual images of the internal organs and tissues, helping in a detailed examination. On the other hand, a PET scan is highly useful in detecting abnormal activity and can provide greater sensitivity compared to other imaging modalities. Moreover, a PET scan can depict changes in the body at an earlier stage. Doctors rely on PET-CT scans to procure extra information regarding cancer and its progression.
What is PET MRI best for?
PET/MRI scans (also called PET/MR scans) are helpful by empowering doctors o make a proper diagnosis and take a call on the best treatment options for diseases like epilepsy, and tumors in the body including the brain.
Is a PET scan better than an MRI?
The principle difference between a PET scan and an MRI or CT scan is that it can provide information on changes at a cellular level and issues with oxygen use, blood flow, and glucose metabolism. It helps in revealing medical conditions at a very early stage.
Is it serious if you need a PET scan?
A patient may need a PET scan to find out if there is cancer. If someone is already diagnosed with cancer, then this test is ordered to see if the cancer treatment is working fine. A PET scan is also ordered to diagnose and monitor heart and brain diseases.
How long do PET scan results take?
When should one get the PET scan findings? After the PET scan, a radiologist carefully examines the scans, prepares a comprehensive report, and forwards it to the consulting doctor. The process takes 24 hours.
Who should I avoid after a PET scan?
The radioactive tracer used during the scan gives out a very minimal level of radiation. However, this radiation gets dissipated very fast. So, to ensure safety, one shouldn’t go closer to pregnant women, infants, and young children for at least six hours after the procedure. If a patient has been given a sedative to induce relaxation, it is imperative to arrange for someone to accompany him/her home and stay overnight.
Why CT scan is better than a PET scan?
The basic difference between them is the focus. A CT scan provides an accurate and detailed image of organs (non-moving), bones, and tissues. On the other hand, a PET scan can help doctors by showing how the tissues in the patient’s body are working at a cellular level.
Why are PET scans so expensive?
PET scans are expensive because the machines are very costly, and they require highly skilled technicians for radiopharmaceuticals used for imaging.









