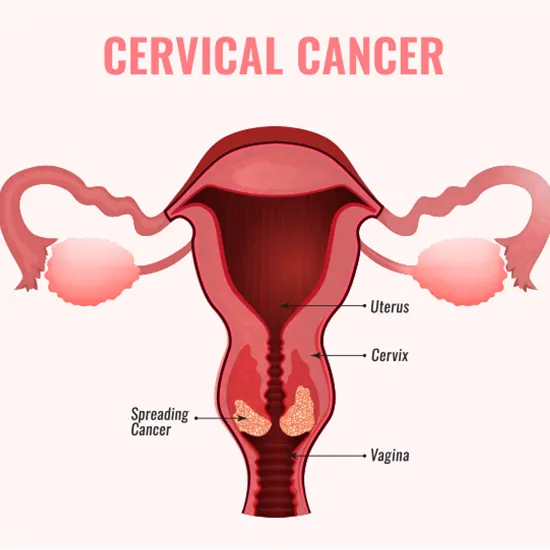
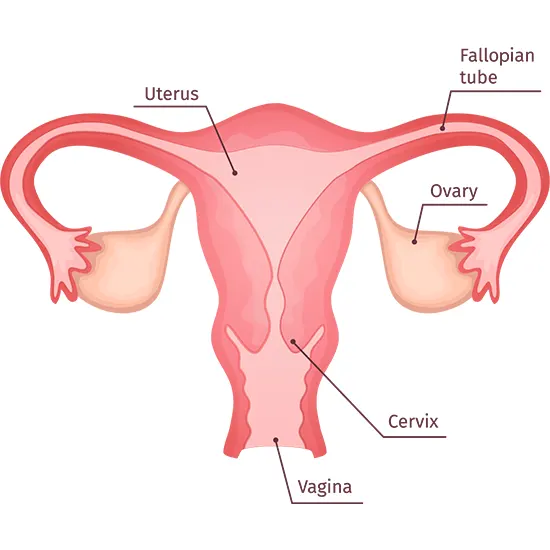
Cervical Cancer develops in the cervix. Cervix is a part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It is usually caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), common sexual transmitted infection.
Cervical Cancer develops in the cervix. Cervix is a part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It is usually caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), common sexual transmitted infection.
Symptoms of cervix cancer
In the early stages, cervical cancer may not cause any symptoms, which is why regular screening is important. However, as the cancer in cervix grows, it causes different signs/ symptoms such as:
Abnormal vaginal bleeding : An abnormal vaginal bleeding that occurs during menses, after sex, or even after menopause.
Unusual vaginal discharge : The foul odor vaginal discharge that is not only watery but bloody too.
Pain during sex : This may be due to the presence of a tumor or infection.
Pelvic pain : This may occur during sex or at other times, and may be caused by the cancer spreading to nearby tissues or organs.
Urinary problems : This includes frequent urination, painful urination, or blood in the urine, which may be a sign that the cancer has spread to the bladder.
Rectal problems : This includes pain, bleeding, or discharge from the rectum, which may be a sign that the cancer has spread to the rectum.
Causes of Cervical Cancer
Cervix cancer (Cervical cancer is primarily caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a common virus that can be transmitted through sexual contact, and it is estimated that around 90% of cases of cervix cancer are caused by HPV. Apart from this, there are some other factors that may increase the risk of developing cervical cancer include:
Smoking : Females who usually smoke is more likely to develop cervical cancer than those who don't smoke.
Weakened immune system : Female with weakened immune systems especially who are suffering from HIV/AIDS or have had an organ transplant.
Sexual activity : Female who have had several sexual partners or who had sex at a young age.
Birth control pills : Females who use oral contraceptives for long term may slightly increase the risk of cervical.
Family history : Females with a family history of cervical cancer.
Environmental factors : Exposure to certain chemicals, such as those found in pesticides, may increase the risk of cervical cancer.
If you have one or more of these risk factors does not mean that you will develop cervical cancer. However, taking steps to reduce these risk factors, such as getting vaccinated against HPV and quitting smoking, may help to lower the risk of developing cervical cancer.
Types of cervix cancer
There are different types of cervical(cervix) cancer include:
Squamous cell carcinoma : This cancer of cervix arises in the flat as well as thin cells that cover the outer surface of the cervix. It accounts for approximately 80-90% of all cervical cancers.
Adenocarcinoma : This cervix cancer type begins in the glandular cells. The glandular cells line the cervical canal. It accounts for approximately 10-20% of all cervical cancers.
Adenosquamous carcinoma : This type of cervical cancer is a combination of both squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma, and it makes up a small percentage of cervical cancers.
Small cell carcinoma : This is a rare and aggressive type of cervical cancer that develops from neuroendocrine cells.
Neuroendocrine carcinoma : This is another rare type of cervical cancer that originates in the hormone-producing cells of the cervix.
Clear cell carcinoma : This is a very rare type of cervical cancer that develops from the clear cells that line the cervical canal.
Stages of cervix cancer
Cervical cancer is classified into different stages based on the extent of the cancerous cells and the spread of the tumor
Stage 0 : This stage, also known as carcinoma in situ, is the earliest stage of cervical cancer, where the abnormal cells are found only on the surface of the cervix.
Stage I : In this stage, cancer is present only in the cervix and has not spread to nearby tissues.
Stage II : In stage II, the cancer has spread to the upper part of the vagina or the tissues around the cervix.
Stage III : In stage III, the cancer has spread to the lower part of the vagina, the pelvic wall, or nearby lymph nodes.
Stage IV : This is the most advanced stage of cervical cancer, where the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the bladder, rectum, or lungs.
The treatment and prognosis for cervical cancer depend on the stage of cancer and other factors, such as the patient's age, overall health, and personal preferences.
Prevention of Cervical Cancer
There are preventive steps that females can take to reduce their risk of cervix cancer:
Get vaccinated : The HPV vaccine is recommended for girls and boys between the ages of 9 and 26
Practice safe sex : Using condoms during sexual activity can reduce the risk of HPV and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Quit smoking : Smoking increases the risk of cervical cancer, so quitting smoking can help to reduce the risk.
Practice good hygiene : Keeping the genital area hygiene by keeping it clean and dry
Get regular screenings : Regular screenings, including Pap tests and HPV testing, can detect abnormal cells in the cervix before they develop into cancer.
Limit sexual partners : Having multiple sexual partners increases the risk of HPV and other STIs, which can increase the risk of cervical cancer.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle : Eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce the risk of cervical cancer.
By taking these steps, women can reduce their risk of developing cervical cancer and improve their overall health. It's important to discuss any concerns about cervical cancer prevention with a healthcare provider.
Benefits of early detection of cervix cancer
Early detection of cervical cancer can lead to better outcomes and a higher chance of successful treatment. Some of the benefits of early detection of cervical cancer include:
Increased treatment options : In the early stages of cervical cancer, there are more treatment options available, including less invasive procedures and a higher chance of a cure.
Higher chance of survival : When cervical cancer is detected early, the five-year survival rate is high, with up to 93% of women surviving five years or more after diagnosis.
Less invasive treatment : Early staged cervical cancer can often be treated with less invasive procedures, such as surgery or radiation therapy, which can help to preserve fertility and sexual function.
Reduced risk of complications : Early detection and treatment of cervical cancer can reduce the risk of complications, such as the need for a hysterectomy, which can have a significant impact on a woman's quality of life.
Better overall health : Early detection of cervical cancer can lead to better overall health outcomes, as it allows for prompt and effective treatment of the cancer, which can improve a woman's quality of life and reduce the risk of other health problems associated with advanced cancer.
Regular screening, including Pap tests and HPV testing, is the most effective way to detect cervical cancer early. Women should discuss their screening options with their healthcare provider and follow the recommended screening guidelines based on their age and risk factors.
Diagnosis of cervix cancer
The diagnosis of cancer of cervical (cervix) involves many steps, including:
Physical exam : A healthcare provider will perform a pelvic exam to look for any abnormalities in the cervix, vagina, or other pelvic organs.
Pap test : A Pap test, or Pap smear, involves collecting cells from the cervix to check for any abnormal cells or signs of cancer.
HPV test : An HPV test involves testing for the presence of the human papillomavirus (HPV), which can cause cervical cancer.
Biopsy : If abnormal cells are detected during the Pap test or if there are other signs of cervical cancer, a biopsy may be performed. During a biopsy, a small sample of tissue is taken from the cervix and examined under a microscope to look for cancer cells.
Imaging tests : If cervical cancer is diagnosed, imaging tests such as, Ultrasound Whole Abdomen, MRI lower abdomen scans, whole body pet scan may be used to determine the area of extent.
Conclusion
It's important for women to undergo regular cervical cancer screenings to help detect any abnormal cells or signs of cancer early. Women should discuss their screening options with their healthcare provider and follow the recommended screening guidelines based on their age and risk factors. Early detection of cervical cancer can improve the chances of successful treatment.
Ganesh Diagnostic and Imaging Centre offers an ideal preventive package for Cervix (cervical cancer). For further information, feel free to contact our expert healthcare executives.









