Book Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) with Capillary Appointment Online Near me at the best price in Delhi/NCR from Ganesh Diagnostic. NABL & NABH Accredited Diagnostic centre and Pathology lab in Delhi offering a wide range of Radiology & Pathology tests. Get Free Ambulance & Free Home Sample collection. 24X7 Hour Open. Call Now at 011-47-444-444 to Book your Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) with Capillary at 50% Discount.
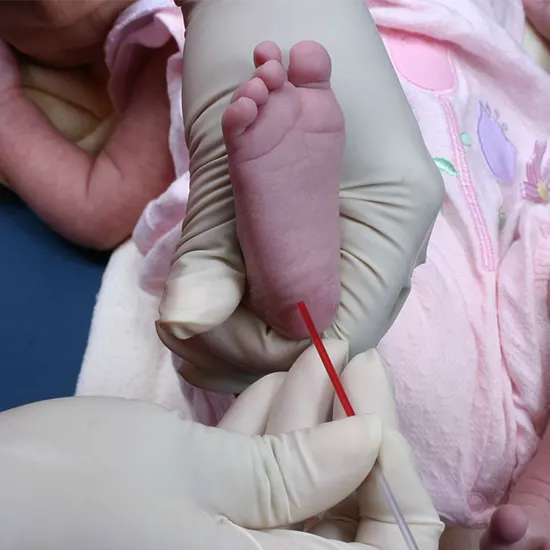
A blood sample is taken from an infant's capillaries as part of a diagnostic procedure called a capillary blood gas (CBG).
In order to determine how effectively the baby is breathing, it is used to evaluate the pH and carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
In this article, we'll go over capillary blood gas collection in general and explain how to analyse the findings.
An infant's capillaries are pricked, and blood is drawn to perform a capillary blood gas (CBG) test. Through the measurement of the blood's pH and carbon dioxide levels, this test examines the neonate's ventilatory condition.
By puncturing the neonate's skin with a tiny needle and removing a drop of blood from the resultant capillary, a capillary blood gas test is carried out.
The best place to puncture a person to obtain capillary blood is on the side of the heel. There are alternative locations that can be used if the heel cannot be reached.
The following potential puncture locations that could be utilised to get a sample of capillary blood are:
Thumbnail Big toe Earlobe
Only if a lateral heel puncture attempt fails would these sites be suggested. In babies, the heel is the best place to inject because of how vascularized it is.
The process of taking a capillary blood gas sample involves the following steps:
| Test Type | Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) with Capillary |
| Includes | Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) with Capillary (Pathology Test) |
| Preparation | |
| Reporting | Within 24 hours* |
| Test Price |
₹ 450
|

Early check ups are always better than delayed ones. Safety, precaution & care is depicted from the several health checkups. Here, we present simple & comprehensive health packages for any kind of testing to ensure the early prescribed treatment to safeguard your health.