Book Imatinib Resistance Mutation Analysis - Kinase Domain Appointment Online Near me at the best price in Delhi/NCR from Ganesh Diagnostic. NABL & NABH Accredited Diagnostic centre and Pathology lab in Delhi offering a wide range of Radiology & Pathology tests. Get Free Ambulance & Free Home Sample collection. 24X7 Hour Open. Call Now at 011-47-444-444 to Book your Imatinib Resistance Mutation Analysis - Kinase Domain at 20% Discount.
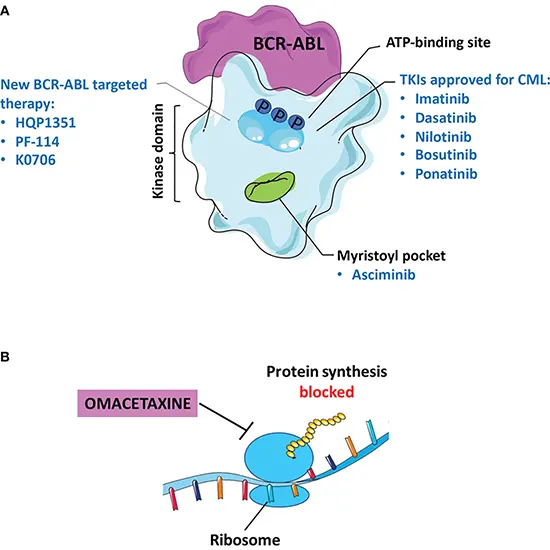
The most often described mechanism for imatinib resistance is the emergence of mutations in the Abl kinase domain. It has been suggested that the source of resistance for many kinase-domain mutations is a direct interference with drug binding.
Patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) who do not respond well to tyrosine kinase inhibitors are thought to benefit from clinical decision algorithms that take into account their BCR-ABL1 kinase domain (KD) mutation status (TKIs).
The majority of nonresponsive patients with CML have mutations in the kinase domain (KD) of ABL1, which are responsible for the most well-studied mechanisms of TKI resistance.
The occurrence of point mutations, which represent a single aa substitution in the kinase domain, which impair drug binding by affecting crucial residues for direct contact with the TKI or by preventing BCR-ABL1 from assuming the inactive state, is the mechanism of acquired resistance to imatinib that is most frequently described.
ABL1 has nuclear localization signals and a DNA binding domain that it employs to mediate DNA damage-repair capabilities, while ABL2 has increased actin and microtubule binding capacity to boost its cytoskeletal remodeling functions.
What does BCR-ABL mutation analysis entail? The fusion of the two genes BCR and ABL leads in the mutation known as BCR-ABL. It's referred to be a fusion gene by some. Chromosome 22 is normally where the BCR gene is found. Chromosome 9 is normally home to the ABL gene. When pieces of the BCR and ABL genes separate and switch locations, the BCR-ABL mutation results.
What does a BCR-ABL result that is positive mean? The diagnosis of B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma and a form of acute lymphoblastic lymphoma (ALL), especially CML, is confirmed.
Rarely, occurrences of acute myeloid leukemia and T-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma are associated with the defective chromosome.
a blood test.
Before any symptoms appear, a complete blood count (CBC) blood test is typically used to identify CML in the majority of patients. A CBC is frequently performed as part of a routine medical examination. White blood cell counts are high in those who have CML.
An abnormal white blood cell count is the most typical indicator of CML and is frequently discovered during blood tests for unrelated medical conditions or during a routine examination. Doctors examine blood and bone marrow cells using a number of tests to determine the presence of CML.
While the rapid and blast phases provide more noticeable symptoms, the chronic phase may produce few or no symptoms. The likelihood of a successful treatment plan increases if CML can be identified and treated by doctors during the chronic phase.
| Test Type | Imatinib Resistance Mutation Analysis - Kinase Domain |
| Includes | Imatinib Resistance Mutation Analysis - Kinase Domain (Pathology Test) |
| Preparation | |
| Reporting | Within 24 hours* |
| Test Price |
₹ 6300
|

Early check ups are always better than delayed ones. Safety, precaution & care is depicted from the several health checkups. Here, we present simple & comprehensive health packages for any kind of testing to ensure the early prescribed treatment to safeguard your health.