A kind of cancer known as uveal melanoma affects the eye, more especially the uvea, the central layer of the eye. It is an uncommon kind of melanoma, making up about 5% of all occurrences. The pigment-producing cells in the...
A kind of cancer known as uveal melanoma affects the eye, more especially the uvea, the central layer of the eye. It is an uncommon kind of melanoma, making up about 5% of all occurrences. The pigment-producing cells in the eye known as melanocytes are where uveal melanoma grows.
Vision loss, floaters, and changes in the pupil's size or shape are only a few of the symptoms of uveal melanoma. Sometimes there may be no symptoms.
Light-colored eyes, pale skin, and a family history of the illness are risk factors for uveal melanoma. Uveal melanoma risk may also be impacted by genetic abnormalities and UV radiation exposure.
Depending on the size and location of the tumor, there are several uveal melanoma treatment options. Radiation therapy, surgery, and occasionally chemotherapy or immunotherapy are all possible forms of treatment. To stop the malignancy from spreading, the eye may occasionally need to be removed (enucleation).
The size and location of the tumor, as well as other elements including the patient's age and general health, might affect the prognosis for uveal melanoma. The five-year survival rate is almost 80% if the malignancy has not progressed past the eye. The prognosis is bleak if cancer has migrated to other bodily regions, though. Patients with uveal melanoma should have regular follow-up treatment to check for any indications of tumor recurrence or metastasis.
This article will give you an in-depth understanding of uveal melanoma.
Know the Commonness
Uveal melanoma is thought to make up roughly 5% of all melanoma cases. Uveal melanoma incidence varies by geographic location and demographic characteristics including age and sex.
Uveal melanoma is thought to occur in about 5 instances per million persons annually in the United States. Men are significantly more likely to experience it than women, and people over 50 are more likely to do so.
Those with fair skin and light-colored eyes, such as those of Caucasian heritage, are more likely to develop uveal melanoma. Also, those who have specific genetic abnormalities, such as those linked to the hereditary cancer syndrome familial atypical mole and melanoma, are more likely to get it (FAMM).
Understanding the causes of Uveal Carcinoma
There is still much to learn about the precise causes of uveal melanoma. The development, however, could be influenced by a mix of hereditary and environmental variables, according to experts.
Genetic factors
Uveal melanoma development has been associated with several genetic mutations. Uveal melanoma, as well as other malignancies including mesothelioma and renal cell carcinoma, have been linked to mutations in the BAP1 gene. Uveal melanoma has also been associated with mutations in other genes, including GNA11 and GNAQ.
Environmental factors
UV radiation from the sun and tanning beds has been linked to an increased risk of skin melanoma, however, it is unclear how UV radiation affects the development of uveal melanoma. While other studies have not identified a strong correlation, others have hypothesized that long-term exposure to UV radiation may raise the incidence of uveal melanoma. Exposure to chemicals, such as pesticides or solvents, has also been explored as an environmental hazard, however, the evidence for a connection with uveal melanoma is weak.
Demographic factors
Those with pale complexion, light-colored eyes (blue, green, or grey), and those of Caucasian heritage are more likely to develop uveal melanoma. Moreover, it is more prevalent in those over 50 and somewhat more prevalent in males than in women.
Hormonal factors
Exposure to estrogen has been mentioned as a potential hormonal risk factor for uveal melanoma. While some research has indicated a substantial relationship between oral contraceptive usage and an increased risk of uveal melanoma in women, other studies have not.
Immune system components
According to certain research, immune system components such as autoimmune disorders and chronic inflammation may raise the risk of uveal melanoma.
Diet factors
While additional study is required to fully support this, there is some evidence to suggest that a diet rich in fruits and vegetables may be linked to a decreased risk of uveal melanoma.
Age-related macular degeneration
Although the data is not yet solid, certain studies have shown a link between age-related macular degeneration and the emergence of uveal melanoma.
Smoking
Although there is conflicting data, smoking has been indicated as a potential risk factor for uveal melanoma.
While these variables may be linked to an increased or decreased risk of uveal melanoma, they do not always cause the condition on their own, it is crucial to keep this in mind. To completely comprehend the intricate interaction of elements that contribute to the development of uveal melanoma, more study is required.
Protect your vision: Knowing the symptoms of uveal melanoma
Knowing the warning signs and symptoms of uveal melanoma is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
Vision changes
Vision changes are the most typical sign of uveal melanoma. This could involve distorted or lost vision in one eye, as well as hazy vision.
Eye pain
Uveal melanoma patients can feel eye discomfort, which can range from moderate to severe. The discomfort might be ongoing or sporadic.
Eye patch:
Uveal melanoma may manifest as a black patch or growth on the iris, choroid, or ciliary body of the eye. This patch might be dark or black in hue and could enlarge with time.
Flashes or Floaters
In the afflicted eye, uveal melanoma may result in flashes of light or floaters.
Redness
Uveal melanoma can occasionally result in redness or edema in the afflicted eye.
Sensitivity to Light
Uveal melanoma patients may experience increased sensitivity to light, making prolonged exposure to bright settings challenging.
Change in Eye Color
Uveal melanoma can occasionally result in a change in the color of the iris, the colorful portion of the eye. Both or just one eye may experience this.
Eye Pain
Some individuals with uveal melanoma may feel pressure or discomfort in the afflicted eye.
Enlarged pupil
Rarely, uveal melanoma may result in an enlarged pupil that doesn't go back to being dilated.
It's critical to remember that not all cases of uveal melanoma exhibit symptoms, and that these symptoms might also be brought on by different eye problems. But, it's crucial to make an appointment with your eye doctor for a full assessment if you experience any of these changes in your vision or eye health. Uveal melanoma can dramatically improve the prognosis and reduce complications with early identification and treatment.
Your eyes deserve a closer look: uveal melanoma diagnosis
Imaging, clinical, and laboratory examinations are frequently used to diagnose uveal melanoma.
Imaging Tests : Imaging tests are performed to see the tumor and figure out where it is and how big it is. These tests might consist of:
Ultrasound
Ultrasound produces pictures of the inside of the eye using sound waves. This examination might reveal the tumor's size and location.
Fluorescein Angiography
Fluorescein angiography is a technique that highlights the blood vessels in the eye by injecting a dye into an arm vein. This examination can measure the tumor's size and locate any regions with unusual blood flow.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT): Using light waves, optical coherence tomography (OCT) may provide pictures of the retina and other internal eye components. This examination can aid in locating retinal or choroid edema or thickening.
Clinical examinations : Clinical examinations are performed to assess the eye and the size of the tumor. These tests might consist of
Test for visual acuity
This procedure assesses your vision's clarity and might reveal any changes in it brought on by the tumor.
Slit-Lamp Exam
In this examination, the front and back of the eye, including the iris, lens, and retina, are examined under a specialized microscope. This can assist in locating and measuring the tumor.
Dilated Eye Exam
The doctor will use eye drops to enlarge the pupil during a dilated eye exam so they can look inside the eye. Any abnormalities, such as a tumor or alterations in the retina, can be found with the use of this.
Laboratory Tests: Laboratory testing is utilized to establish cancer's stage and confirm the diagnosis of uveal melanoma. These tests might consist of:
Biopsy
A biopsy is removing a little sample of tumor tissue and studying it under a microscope. This can establish the presence of cancer cells and validate the diagnosis of uveal melanoma.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can be conducted to look for any aberrant blood cell counts that can reveal the cancer's stage and severity.
Overall, uveal melanoma is diagnosed and the appropriate course of therapy is chosen using a mix of imaging studies, clinical exams, and laboratory testing. Regular eye exams are crucial, as is getting medical help if you detect any changes in your eyesight or eye health.
A Comprehensive treatment plan for Uveal Melanoma
The size and location of the tumor, whether it has spread to other areas of the body, and the patient's general condition all affect how uveal melanoma is treated.
Surgery
For tiny tumors or those that are restricted to a single location of the eye, surgery may be advised. A thyroidectomy is the most popular surgical treatment for uveal melanoma and entails removing the choroid's afflicted portion (the blood-rich layer of tissue in the eye). The entire eye may need to be removed in rare circumstances (enucleation). Enucleation is a significant procedure that is often used to remove bigger tumors or that cannot be removed using other techniques.
Radiation therapy
Using high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells, radiation therapy is a frequent treatment for uveal melanoma. Radiation treatment comes in two major forms:
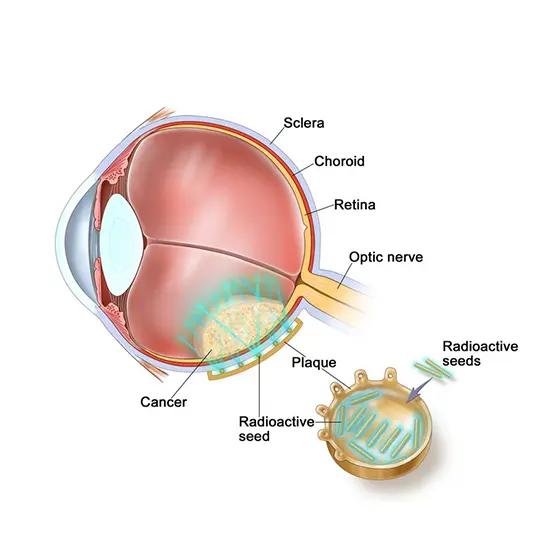
Brachytherapy
In brachytherapy, a tiny radioactive device (plaque) is positioned on the surface of the eye, close to the tumor. The plaque is then removed after the radiation has been administered over several days.
External Beam Radiation Therapy
In external beam radiation therapy, the tumor is exposed to high-energy radiation beams from the outside. Usually, this therapy is given over many weeks.
Medications : Uveal melanoma that has migrated to other body areas can occasionally be treated with medicine. Chemotherapy or medicines used in targeted therapy may be among these medications. These therapies, which can be administered orally or intravenously, are frequently combined with surgery or radiation treatment.
It's crucial to be aware that uveal melanoma therapy may cause adverse effects including vision abnormalities, eye dryness or irritation, or weariness. To make sure you get treatment, it is crucial to communicate any worries or inquiries with your healthcare staff.
The hidden dangers of uveal melanoma: Complications you need to know
Depending on the tumor's size and stage, as well as if it has spread to other body areas, the problems of uveal melanoma might change. Here are a few potential side effects of uveal melanoma:
Vision Issues
Vision loss, glaucoma, retinal detachment, cataracts, and other eye-related complications can all be brought on by uveal melanoma. Glaucoma damages the optic nerve.
Metastasis
Uveal melanoma can extend to the liver, lungs, and bones, among other organs. Many consequences may result from this, such as organ failure, excruciating pain, and a higher possibility of developing additional medical issues.
Treatment-related adverse effects
Surgery or radiation therapy used to treat uveal melanoma may cause minor to severe side effects. A few of these include vision abnormalities, eye dryness or discomfort, weariness, and skin changes.
Complications on an emotional level
Receiving a diagnosis of uveal melanoma can be emotionally taxing and may result in anxiety, despair, and stress. The physical health of a person may suffer as a result of these emotional difficulties.
If you have any questions regarding uveal melanoma or its potential side effects, it's crucial to see a medical expert. Increased success rates can be achieved with early identification and treatment.
Don't Let Uveal Melanoma Steal Your Vision; Together We Can Beat Uveal Melanoma: Join the Fight Now.









