Meningitis is a serious illness that can beget inflammation of the filling around the brain and spinal cord. This inflammation can be caused by a variety of factors, including contagions, fungi, and bacteria. Of these,...
Meningitis is a serious illness that can beget inflammation of the filling around the brain and spinal cord. This inflammation can be caused by a variety of factors, including contagions, fungi, and bacteria. Of these, bacterial meningitis is the most severe and can lead to endless brain damage, hair loss, learning disabilities, and indeed death.
It's critical to comprehend the signs, causes, and available therapies for this potentially fatal condition. In this post, we’ll discuss what bacterial meningitis is, how it's diagnosed, the common symptoms, and the stylish course of treatment to help you or a loved one stay informed and take precautionary measures.
1. What's bacterial meningitis?
Bacterial meningitis is a serious and potentially life- hanging infection that affects the meanings, which are the defensive membranes that compass the brain and spinal cord. This type of meningitis is caused by colorful bacteria, including Streptococcus pneumonia, Neisseria, and haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib).
Bacterial meningitis is a contagious complaint and can be spread through contact with respiratory or throat concealment, similar to slaver, mucus, or nasal discharge. Additionally, kissing, coughing, or sneezing close to someone who is ill can transfer it.
People who are at an advanced threat of constricting bacterial meningitis include babies, youthful children, and teenagers, as well as people with weakened vulnerable systems or those who have had close contact with someone infected with the complaint.
Symptoms of bacterial meningitis can vary, but frequently include fever, headache, neck stiffness, puking, and perceptivity to light. However, bacterial meningitis can lead to severe complications, similar as brain damage, if left undressed.
Treatment options for bacterial meningitis generally involve hospitalization and the administration of intravenous antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. In severe cases, probative care, similar to respiratory support and fluid operation, may also be needed.
If you or someone you know may have bacterial meningitis, it's critical to seek immediate medical assistance. Early opinion and treatment can greatly ameliorate the chances of a full recovery.
2. The symptoms of bacterial meningitis?
Bacterial meningitis is a serious medical condition that can progress fleetly if not treated instantly. It's important to be apprehensive of the symptoms so that you can seek medical attention incontinently if you suspect you or someone you know may have the infection.
Depending on the patient's age, bacterial meningitis can present with a variety of symptoms, but some of the most common symptoms include an unforeseen onset of high fever, severe headache, neck stiffness or pain, perceptivity to light, confusion or altered internal status, nausea or vomiting, and a skin rash.
In babies, the symptoms of meningitis can be more delicate to describe and may include perversity, poor feeding, high-pitched weeping, and a bulging fontanelle( soft spot on the top of the head). It's crucial to remember that not everyone who has meningitis will exhibit all of these symptoms, but if you or someone you know is passing any combination of these symptoms, seek medical attention incontinently.
3. Causes of bacterial meningitis?
A bacterial infection that affects the brain and spinal cord is the cause of bacterial meningitis. The most common bacteria that beget meningitis are Streptococcus pneumonia, Neisseria, and Haemophilus influenzae type b. These bacteria are generally set up in the nose and throat of healthy individuals and are generally inoffensive.
Still, in some cases, they can foray the bloodstream and spread to the brain and spinal cord, causing meningitis. Bacterial meningitis can also be caused by other types of bacteria, similar as Serum Electrolytes Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli (E. coli). These bacteria are generally associated with food- borne ails, but they can also beget meningitis in certain cases Bacterial meningitis is an infectious condition that can be passed from person to person by being in close proximity to an individual who has it.
This can happen through coughing, sneezing, or kissing. People who live in close diggings, similar as council dorms or military barracks, are at an advanced threat of contracting the complaint.
Remember that not all bacterial infections result in meningitis. In fact, most people who are exposed to these bacteria don't develop the complaint. Still, certain factors can increase the threat of developing meningitis, similar as a weakened vulnerable system, a recent head injury, or a history of meningitis in the family.
Understanding the causes of bacterial meningitis is pivotal in precluding the spread of the complaint. Vaccines are available for some types of bacteria that beget meningitis and rehearsing good hygiene, similar to frequently washing your hands and protecting your mouth when you sneeze or cough can also help reduce the threat of infection.
4. How bacterial meningitis is diagnosed?
Bacterial meningitis is a serious condition that requires prompt opinion and treatment to help complications. The opinion of bacterial meningitis is grounded on a combination of patient history, physical examination, and individualtests.However, the healthcare provider will perform a physical test of the case to check for symptoms similar to fever, headache, if meningitis is suspected.
During the physical test, the healthcare provider will also check for signs of brain swelling or inflammation, similar to changes in internal status, confusion, or seizures. To confirm the opinion, the healthcare provider may order several tests, including blood tests, a lumbar perforation (spinal valve), and a x-ray CT checkup or MRI of the brain.
The lumbar perforation is a sample of the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord, called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The CSF is also anatomized to confirm the presence of bacteria and determine which type of bacteria is causing the infection. This information is pivotal in determining the applicable treatment course for the case.
It's important to note that early opinion and treatment are essential in managing bacterial meningitis. Any detention in opinion can lead to serious complications including brain damage, hair loss, and indeed death. However, seek medical attention incontinently, if you suspect that you or a loved one may have bacterial meningitis.
5. Treatment options for bacterial meningitis?
Bacterial meningitis is a serious and life- hanging illness that requires immediate medical attention. The inflexibility of the infection, the type of bacteria that caused the infection, and other factors affect bacterial meningitis treatment options, and the age and overall health of the case.
Antibiotics are the primary treatment for bacterial meningitis. The type of antibiotic specified will depend on the type of bacteria causing the infection to treat the infection properly a combination of antibiotics could be required in some circumstances. In addition to antibiotics, other therapies may be required to treat problems and control symptoms. For illustration, cases with severe headache and fever may be given specifics to reduce pain and fever.
Fluids may also be administered to help dehumidification. Cases with severe infections may bear hospitalization for close monitoring and ferocious treatment. Surgery may occasionally be required to drain accumulated brain fluids or to clear an infection. If you believe that you or someone you know may have bacterial meningitis, it's critical to get medical care as quickly as possible. With timely opinion and applicable treatment, the chances of a full recovery are much advanced.
6. Common myths about bacterial meningitis?
There are numerous myths surrounding bacterial meningitis, and it's important to separate fact from fabrication in order to better understand the complaint. Then are some common myths about bacterial meningitis
- Myth# 1
Bacterial meningitis only affects children. While bacterial meningitis is more common among children under the age of five, people of all periods can get the complaint.
- Myth# 2
Bacterial meningitis isn't contagious. Bacterial meningitis is largely contagious and can spread through close contact with an infected person’s slaver or other fleshly fluids.
- Myth# 3
Bacterial meningitis isn't treatable. Bacterial meningitis is a serious illness, but it's treatable with antibiotics. Early treatment is critical to help serious complications and reduce the threat of death.
- Myth# 4
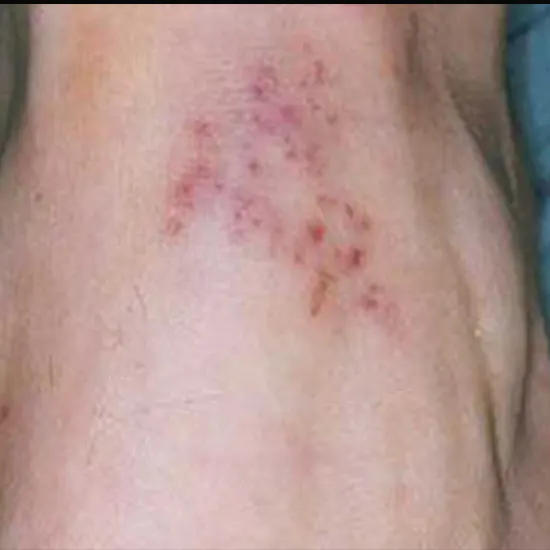
Bacterial meningitis always causes a rash. While a rash is a common symptom of meningococcal meningitis (a type of bacterial meningitis), not all types of bacterial meningitis beget a rash.
It's important to educate yourself and others about the data surrounding bacterial meningitis in order to cover yourself and your loved ones. However, seek medical attention incontinently, if you think you, someone you know, or someone else may have bacterial meningitis.
Thank you for taking the time to read our composition on bacterial meningitis. We know that this is a serious illness and that numerous people have questions about it. We hope that we’ve handed you with a better understanding of the symptoms, causes, and treatment options available.
However, it's essential to seek medical attention incontinently, if you suspect that you or someone you know may have bacterial meningitis. Flash back, early opinion and treatment can save lives! Stay healthy and stay safe.









