Ovarian germ cell tumors (OGCTs) are heterogeneous tumors that are inferred from the primitive germ cells of the embryonic gonad, which accounts for around 2.6% of all ovarian malignancies.
Ovarian germ cell tumors (OGCTs) are heterogeneous tumors that are inferred from the primitive germ cells of the embryonic gonad, which accounts for around 2.6% of all ovarian malignancies. There are four fundamental sorts of OGCTs, specifically dysgerminomas, yolk sac tumors, teratoma, and choriocarcinoma.
Dygerminomas are Threatening germ cell tumors of the ovary and are especially noticeable in patients analyzed with gonadal dysgenesis.OGCTs are moderately troublesome to identify and analyze at an early arrange since of the nonspecific histological characteristics.
Common side effects of OGCT are bloating, stomach distention, ascites, and dyspareunia.OGCT is caused basically due to the arrangement of dangerous cancer cells within the primordial germ cells of the ovary. The correct pathogenesis of OGCTs is still obscure be that as it may, different hereditary transformations and natural variables have been identified.
OGCTs are commonly found during pregnancy when an adnexal mass is found amid a pelvic examination, ultrasound checks appear a strong mass in the ovary, or blood serum test appears hoisted alpha-fetoprotein levels. They are unlikely to have metastasized and thus the standard tumor administration is surgical resection, coupled with chemotherapy. The event rate is less than 3% around the world.
Classification of Germ Cell Tumour
OGCTs can be classified into dysgerminoma, teratomas, yolk sac tumors, and choriocarcinomas, recorded within the arrange of predominance.
Dysgerminoma
Dysgerminomas are comparable to testicular seminomas and account for around 32- 37% of all OGCTs.They are especially noticeable in people with dysgenic gonads of 46, XY unadulterated gonadal dysgenesis patients. Based on net examinations, dysgerminomas are characterized by having a 'solid, lobulated, tan, flesh-like net appearance with a smooth surface'.
Microscopically, the cellular structure is recognized by a round-ovoid shape containing sufficient eosinophilic cytoplasm and sporadically formed nuclei. The consistently situated cells are isolated through the stringy strands and lymphocytic invasion is commonly watched.
Teratomas
Teratomas are the most common germ cell tumors of the ovary. Teratomas can be separated into two sorts: develop teratoma (generous) and youthful teratoma (harmful). Juvenile teratomas contain youthful or embryonic tissue which essentially separates them from developed teratomas as they carry dermoid blisters.
It is commonly watched in 15 to 19-year-old ladies and seldom in ladies after menopause. Immature teratomas are characterized by a distance across 14–25 cm, typified mass, cystic ranges, and periodic appearance of hemorrhagic ranges. The organization of juvenile teratomas is decided to depend on the sum of juvenile neuroepithelium tissue recognized.
Yolk sac tumor
The ovarian yolk sac tumors, too known as endodermal sinus tumors, are responsible for roughly 15.5% of all OGCTs.They have been watched by ladies, especially in their early ages, and once in a while after 40 a long time of age. The basic pathologic highlights are a smooth outside surface and capsular tears due to their quick rate of development.
A consideration comprising 71-person cases of ovarian yolk sac tumors gives proof of the expansion of the tumor. In one of the cases, the pelvic examination uncovered typical movement until a 9 cm and 12 cm measured tumor was found 4 weeks afterward. In another case, a 23 cm tumor was found in a pregnant lady who was checked routinely and had ordinary discoveries until an oophorectomy got to be essential.
Histologically, these tumors are characterized by blended strong and cystic components. The blended strong components are characterized by delicate gray to yellow strong components that went with critical hemorrhage and rot. The blisters are roughly 2 cm in breadth and populated all through the tissue which comes about in giving the neoplasm a 'honeycombed appearance'.
Choriocarcinoma
Choriocarcinomas are outstandingly uncommon and account for 2.1%-3.4% of all OGCTs.Under net examination, the syncytiotrophoblast cells are adjusted in a plexiform course of action with the mononucleated cytotrophoblast cells encompassing the foci of the hemorrhage. Choriocarcinomas can be partitioned into gestational choriocarcinomas and non-gestational choriocarcinomas which have immunohistochemical contrasts.
Signs and Symptoms of Ovarian Germ Cell Tumour
OGCTs are generally troublesome to identify and analyze at an early arrange basis since the side effects are regularly inconspicuous and nonspecific. They ended up recognizable when as they ended up huge, unmistakable masses. Side effects incorporate bloating, stomach distention, ascites, and dyspareunia. In uncommon cases where the tumor bursts, intense stomach torment can be experienced.
The basic marker of threat is ordinarily the appearance of Sister Mary Joseph Nodule.OGCTs can encourage provide rise to ovarian torsion, hemorrhage, and indeed isosexual bright adolescence in youthful children.
Causes of Ovarian Germ Cell Tumour
The precise cause of OGCT is however to be determined. In any case, several variables have been recognized which may contribute to the expanded hazard of OGCTs counting endometriosis, polycystic ovarian disorder, and hereditary hazard factors. Individuals who are more inclined to create OGCTs more often than not contain the autosomal prevailing, BRCA-1/ BRCA-2, mutations.Complications with other cancers such as genetic nonpolyposis colorectal cancer, too known as Lynch disorder, increments the hazard of creating ovarian cancer.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and verbal contraceptives are known to have diminished hazards for OGCTs.The etiology of OGCT is still under ponder, be that as it may, hereditary modifications may contribute to the advancement of OGCTs, such as the classical tumor silencer qualities and oncogenes.
On the side of hereditary alterations, certain natural variables such as endocrine disruptors, nearness of an everyday schedule that influences the individual's natural chemistry, and introduction to maternal hormones may moreover contribute to the multiplication of OGCT. A later ponder on rats appeared the transgenerational epigenetic legacy supporting the impact of dangerous natural substances, counting plastics, pesticides, and dioxins, on the pathogenesis of OGCT.
Pathogenesis of Ovarian Germ Cell Tumour
In any case, many hypotheses for the causes have been made. Amid ovulation, the follicle cracks come about in epithelial cell damage. In arrange to mend the tissue and supplant the harm, the cells experience cell division.
Each time the cell isolates, there's a plausibility for changes to happen and the chance of tumor formation increases. The tumor is caused when the germ cells within the ovaries start partitioning wildly and ended up threatening which are characterized by their less organized cores and unclearly characterized border. Another potential etiology is the dysfunctioning of the tumor silencer quality, TRC8/RNF139, or indeed karyotypic anomalies after near atomic examination.
OGCT has its roots in embryonic advancement where the primordial germ cells (PGCs) are separated in early stages and can modify the genome as well as the transcriptome. OGCTs can be credited to the inside component of PGCs and their changing characteristics.
Staging of Ovarian Germ Cell Tumour
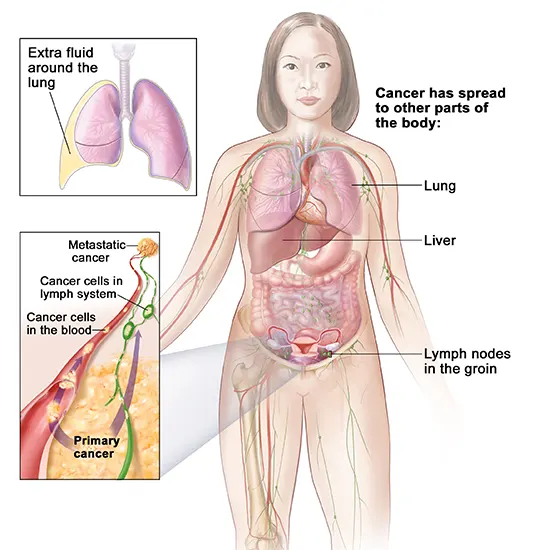
After OGCT has been analyzed, different tests will be conducted to decide whether cancer has spread to other regions within the body. The spread of OGCT is distinguished through diverse stages: StageI, StageII, StageIII, and Stage IV to be specific.
StageI: Tumor cells are localized within the ovaries or the fallopian tubes without broad spread to other body locales.
StageII: The cancer is in one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes and has spread into the pelvis.
StageIII: Cancer has spread past the pelvis into the guts and to the retroperitoneal lymph hubs (found at the back of the guts). The substages are characterized by the relative estimate of the tumor. Note:
StageII ovarian cancer will moreover be pronounced in case the cancerous cells have spread to the liver.
Stage IV: Cancer has spread the exterior of the guts and pelvis to more removed organs, such as the lungs.
Diagnosis of Ovarian Germ Cell Tumour
The preparatory determination starts with a pelvic examination, serum tumor marker test, and imaging. Doctors may feel an expansive discernable mass or protuberance in the lower midriff upon the addition of the gloved fingers into the vagina.
To encourage distinguishing the histologic subtypes of OGMTs, blood tests of patients are collected to examine the serum level of biomarkers discharged by the tumor cells. A surge within the plasma levels of human chorionic gonadotropin and alpha-fetoprotein is characteristic of OGMTs.Lactate dehydrogenase, soluble phosphatase, and cancer antigen 125 might potentially increase as well.
To imagine the area and morphology of the tumor, transvaginal ultrasonography is as a rule employed. The most characteristic appearance could be a parenchymal-like hyperechoic mass with sharp borders and tall vascularization. Computed tomography would create a stacked picture interior of the peritoneal locale of the body to envision the lobular design of the tumor.
Usually, for dysgerminoma, a strong mass being compartmentalized into lobules with upgrading septa may be apparent for discharge or corruption.
Preoperative procedures
In understanding FIGO organizing rules, comprehensive surgical arranging will be conducted to look at the degree of tumor spread through peritoneal locales or lymph drainages.
28% of arrange II patients will be found with the improvement of auxiliary harmful developments at lymph hubs separate from an essential location of cancer, called lymph hub metastasis.
There are three major lymphatic drainage pathways
- waste to the paraaortic lymph hubs through ovarian veins
- seepage from the wide tendon to the iliac lymph hubs
- seepage from the circular tendon to the inguinal lymph hubs
Palpation or biopsies of one-sided pelvic and para-aortic lymph hubs will be conducted as a preoperative step to infer the guess of the tumor and lymphatic spread.
Peritoneal biopsies and omentectomy will also be utilized to assess the degree of tumor substance spillage or implantation in the peritoneal cavity. Tumor cells may shed off from the first location into the peritoneal depth and embed onto the liver capsule surface or diaphragm.
They may clog up the interior of the lymphatic vessel around the stomach and anticipate the resorption of peritoneal fluid. In the conclusion, pericardiophrenic lymphadenopathy and ascites may result from this straight-to-the-point intrusion.
Epidemiology
OGCT could be an uncommon tumor beneath the scope of ovarian cancer, bookkeeping for less than 5% of all ovarian malignancies. It happens generally in 15-19-year-old ladies and appears 75% rate for ladies matured <30 a long time.
In 2011, the number of modern cases that happened around the world is 5.3 per million. In most nations, the event rate on normal is less than 3% of the population. However, Asia has detailed the most elevated extent of cases up to 4.3% due to the more youthful age profile of the population. For other districts, the frequency rates detailed are 2.5% in Oceania, 2.0% in North America, and 1.3% in Europe.
The five-year survival rates have come to up to 90-92%, which is much higher than that of epithelial ovarian cancers. The primary reason is the tall adequacy of platinum-based chemotherapy.
Treatment of Ovarian Germ Cell Tumour
Surgery
Threatening OGCTs are transcendently one-sided and chemosensitive, which suggests they are localized in as it were one side of the ovary. Fertility-preserving surgery is fundamentally standardized to keep the contralateral ovary and fallopian tube intaglio, moreover known as a one-sided salpingo-oophorectomy.
For Stage II patients with discernible metastasis, cytoreductive surgery may be performed to debulk the volume of the tumor, such as a hysterectomy (evacuation of all or portion of the uterus) and reciprocal salpingo-oophorectomy. A surgical cut at the stomach depression after the completion of adjuvant chemotherapy, called moment-see laparotomy, is best appropriate for patients detailed with teratomatous components after past cytoreductive surgery.
Adjuvant Chemotherapy
With a repeat of up to 15-25% for early-stage patients, adjuvant chemotherapy ought to couple with surgical resection of the tumor to guarantee full rescue. For systemic chemotherapy (issued orally or intravenously), the regimen is institutionalized in each FIGO organized to contain bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin, too known as the BEP treatment.
Patients ought to be issued with 3-4 cycles of BEP to guarantee full rescue. Depending on the customized conditions, a few patients who are non-responders to BEP treatment will be endorsed with rescue treatment, which comprises cisplatin, ifosfamide, and paclitaxel. Yet, it is likely that OGCT survivors after BEP treatment will have untimely menopause at the harsh age of 36. Alternatively, a few healing centers were selected for platinum-based chemotherapy since the platinum complexes shown within the sedate mediate DNA translation by shaping chemical cross-links inside the DNA strands, which avoids the generation of cancerous cells.
The major components are cisplatin, carboplatin, and oxaliplatin. It has been detailed with full recuperation among early-stage patients and as it were a quarter of advanced-stage patients are not rescued possibly due to sedate resistance.
For advanced-stage patients, after cytoreductive surgery, imperceptible tiny cancerous cells or knobs may still be displayed at the location of infection. Therefore, specialists may instill a warmed chemotherapy arrangement (~42-43 °C) into the stomach depth through carters tubes for 1.5 hours. Based on the rule that cancer cells regularly pass on at 40 °C, substantial cells remain unaffected since they kick the bucket at 44 °C.
This novel strategy is demonstrated successful with as it were 10% repeat rate and no mortality recorded. It is known as hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC), containing docetaxel, and cisplatin. Given the sedate is spread locally in intraperitoneal locales, it has no systemic side impacts on other effectively replicating cells and is favored over systemic chemotherapy.
Regularly, wild sedate conveyance in systemic chemotherapy comes about in myelosuppression, particularly with watched febrile neutropenia, neurotoxicity, ototoxicity, and nephrotoxicity. Remedial medicines to bargain with chemotherapy-induced toxicities are through the infusion of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor or myeloid development variables or verbal admissions of prophylactic anti-microbials.









