
Polycystic Kidney Disease is a genetic inherited disorder in which thousands of cysts grow in the kidney. Cysts in the kidney cause impaired kidney function and potential kidney failure. Generally both kidneys are affected...
Polycystic Kidney Disease is a genetically inherited disorder in which thousands of cysts grow in the kidney. Cysts in the kidney cause impaired kidney function and potential kidney failure. Generally both kidneys are affected with PKD but one kidney may develop the cysts earlier than the other. As the cysts grow in number and size, it reduces the healthy kidney tissue. This makes it harder for your kidney to work in a proper manner.
As it affects males and and females in equal numbers, and the cysts may appear at any age, depending on the type of Polycystic Kidney disease. These cysts can vary in size and can develop in other body parts or on organs like Liver.
Polycystic Kidney disease is diagnosed by blood tests, ultrasounds of the kidney, CT Scan, and MRI scans. As the age increases the size and number of the cysts increases. So a genetic test is a key diagnostic test to detect the mutations to confirm the diagnosis.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for polycystic kidney disease. Treatment generally involves symptomatic treatment and preventions are taken for the complications and to stop or prevent the progression of the disease.
This kidney disease may cause renal failure or end-stage renal failure. We at Ganesh Diagnostic provide the best kidney diagnostic tests.
What is Polycystic Kidney Disease?
Polycystic Kidney diseases are a group of genetic disorders and a leading cause of kidney failure. It is characterised by the progressive bilateral formation of renal cysts. As the cysts become larger, the kidneys lose their ability to filter waste from the blood, which leads to progressive loss of kidney function or eventually kidney failure.
What Are the Causes of PKD?
PKD is a genetic inherited disorder. There are three types of polycystic Kidney diseases,
Autosomal Dominant PKD
ADPKD is also known as adult PKD. A parent with autosomal dominant PKD has a 50% chance of passing on to each of their offspring the mutated gene (PKD1 or PKD2) and the related illness. The gene never skips a generation, so if an individual does not inherit it, there is no chance that their offspring will either.
Sometimes, persons develop PKD with no family history, it may be due to change in genetics. ADPKD can lead to renal failure or kidney failure.
Hence, it is important to seek doctor consultation as early as possible.
Autosomal recessive PKD
Autosomal recessive PKD is a significant hereditary renal disease in childhood. Symptoms of ARPKD are generally diagnosed in utero or in the early childhood phase. It is characterised by the enlarged echogenic kidneys in disease fetuses. Because of this, it is also known as infantile PKD. Children who are born with polycystic kidney disease commonly develop kidney failure within a few years of the birth and they may experience liver problems as they grow into adults.
Acquired cystic kidney disease
“Acquired” word itself “is not inherited”. Initially, doctors might order a urinalysis to check for blood, bacteria, or protein in your urine and a complete blood count to check for anemia or infection symptoms.
Your doctor may check for kidney, liver, and other organ cysts using imaging tests in order to diagnose all three forms of PKD.
What are the Symptoms of PKD?
Symptoms of Polycystic Kidney disease across the different types are:-
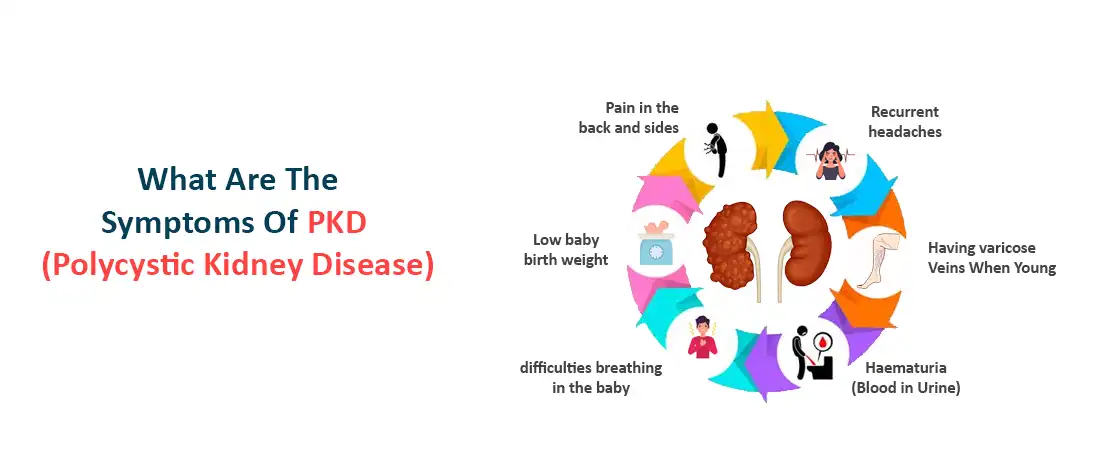
- Haematuria (blood in urine)
- Pain in the back and sides
- Swollen belly or abdomen due to an enlarged kidney
- Recurring urinary tract infections, including Kidney and bladder infections
- Elevated blood pressure or hypertension
- A sensation of pounding or fluttering in the chest brought on by malfunctioning valves
- Recurrent headaches
- Low baby birth weight
- Low amniotic fluid levels, which reduce the baby's uterine urine production
- difficulties breathing in the baby
- Baby regurgitates formula or breast milk after being fed
- incorrect development and growth of the baby's face, arms, and legs
- Having varicose veins when young
- Reduce the child's weight and height as they grow
What Are the Complications From PKD?
- Kidney Stones
- Early satiety and gastroesophageal reflux
- Shortness of breath
- Hypertension that does not go away
- Cysts in the liver or pancreas
- As the disease progresses the disease may lead to end-stage renal disease.
- It may lead to heart conditions
- Aneurysms in the brain (a bulging blood vessel)
- Preeclampsia in pregnant women (a type of hypertension)
- Liver damage, but as the disease progresses it may lead to liver failure.
- Fatality, in infants with ARPKD
- Urinary tract infections that keep recurring
How to Diagnose Polycystic Kidney Disease?
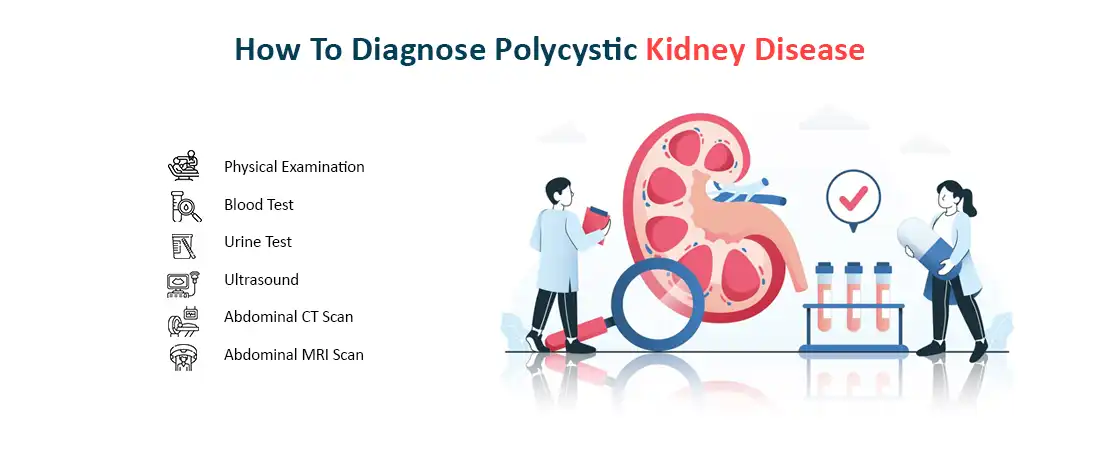
Diagnosis of Polycystic Kidney disease is typically made from family history consistent and multiple kidney cysts bilaterally. Diagnosis of Polycystic Kidney Disease may involve a number of tests including:-
- Physical Examination- detect symptoms such as high blood pressure or enlarged kidney
- Blood Test- To assess the function of the kidney (KFT Test)
- Urine Test- if there is blood, protein, or both may be found in the urine.
- Ultrasound- Renal ultrasonography or abdominal ultrasound uses sound waves to detect the presence of cysts in the kidney.
- Abdominal CT Scan- This diagnostic test detect the presence of cysts even smaller cysts in the kidney
- Abdominal MRI Scan- The MRI scan is used to detect the strong magnets to evaluate the kidney structure and presence of cysts. It is mainly used to detect complications such as bleeding or kidney stones.
How to Treat Polycystic Kidney Disease?
Depending on how the condition progresses, doctors may employ the following therapies for polycystic kidney disease.
Controlling blood pressure: One of the main signs of polycystic kidney disease is elevated blood pressure. Your physician works with you to manage it with medication, physical activity, and diet to avoid heart failure and stroke.
The majority of babies who require breathing support have undeveloped lungs.
Dialysis: Hemodialysis, in which the blood is filtered outside the body, or peritoneal dialysis, which uses the stomach lining and a special fluid, is used for patients with kidney failure.
Growth therapy: Underweight babies may need nutritional therapy or human growth hormone to help them grow.
Pain management: Painkillers are used to treat headaches, kidney stones or bursts, and infections-related pain. Drugs purchased over-the-counter may harm the kidneys. Make sure the safest medications are prescribed by your physician.
Kidney transplant: Should the illness worsen to the point of end-stage renal failure, you may need a replacement kidney.
Conclusion
An inherited condition called polycystic kidney disease is detectable, typically through ultrasonography, and is brought on by genetic mutations. Although there are at-home genetic tests available at Ganesh Diagnostic And Imaging Centre, it is not advised to use them as the accuracy of the tests to identify PKD is often questionable. Furthermore, people with a known family history of Parkinson's disease (PKD) should be aware of the disease's symptoms and seek medical attention from a professional if they worsen.
A Note Ganesh Diagnostic And Imaging Centre
Anyone who has the possibility of PKD can be overwhelming and upsetting. As PKD runs in your family, work with a medical specialist who specializes in kidney diseases. Such as a nephrologist can be crucial. Well, it is important to diagnose as early as possible.
Ganesh Diagnostic and Imaging Centre is one of India's Foremost diagnostic centres. As they provide comprehensive multidisciplinary diagnostic service for everyone. At Ganesh Diagnostic you can expect patient-focused, comprehensive care with Free Ambulance service and Free home sample collection service.
We also provide Free doctor consultations.
Book your appointment today with us
For queries contact us, 24X7









