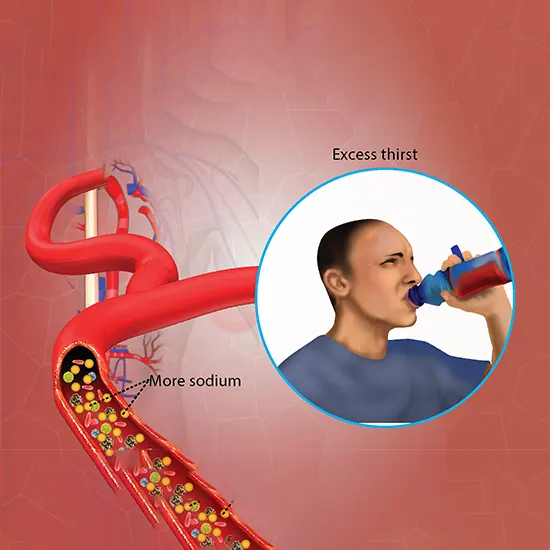
Hypernatremia, too spelled hypernatremia, could be a tall concentration of sodium within the blood. Early side effects may incorporate a solid feeling of thirst, shortcomings, queasiness, and misfortune of appetite. Serious...
"Salty secrets: Uncovering the dangers of Hypernatremia"
What is Hypernatremia?
Hypernatremia, too spelled hypernatremia, could be a tall concentration of sodium within the blood. Early side effects may incorporate a solid feeling of thirst, shortcomings, queasiness, and misfortune of appetite. Serious indications incorporate perplexity, muscle jerking, and dying in or around the brain. Hypernatremia is by and large characterized as a serum sodium level of more than 145 mmol/L. Extreme side effects regularly as it happened when levels are over 160 mmol/L.
Epidemiology of Hypernatremia?
Hypernatremia is fundamentally seen in newborn children and the elderly populace. Untimely newborn children are at higher hazard due to their generally little mass to surface zone and their dependency on the caretaker to manage liquids. Patients with neurologic impedance too are at chance due to impeded thirst components and lack of water accessibility. Hypernatremia can happen within the healing center setting due to hypertonic liquid implantations, particularly when combined with the patient's failure for satisfactory water admissions.
Hypernatremia
Hypernatremia is ordinarily classified by a person's liquid status into moo volume, typical volume, and tall volume.
Moo blood protein levels can result in an erroneously tall sodium measurement. The cause can more often than not be decided by the history of events. Testing the pee can offer assistance if the cause is unclear. The fundamental component regularly includes as well small free water within the body. In case the onset of hypernatremia was over many hours, at that point it can be adjusted moderately rapidly utilizing intravenous ordinary saline and dextrose in water.
Something else, rectification ought to happen gradually with, for those incapable to drink water, half-normal saline.
Hypernatremia due to diabetes insipidus as a result of brain clutter may be treated with the medicine desmopressin. If the diabetes insipidus is due to kidney issues the medicine causing the issue may require to be ceased or the fundamental electrolyte unsettling influence corrected. Hypernatremia influences 0.3–1% of individuals in the hospital. It most frequently happens in babies, those with impeded mental status, and the elderly. Hypernatremia is related to an expanded chance of passing but it is vague if it is the cause.
How Does the Body Control Sodium Levels?
Sodium is an electrolyte that plays a basic part in controlling levels of water and other substances within the body. The kidneys and adrenal organs are dependable for directing sodium levels. The adrenal organs deliver a hormone called aldosterone. This hormone and the kidneys work together to preserve the adjustment of sodium within the blood. Changes in water misfortune or water intake alter the concentration of sodium within the blood. Receptors within the brain at that point recognize the requirement for level redresses. The body reacts by either expanding thirst to boost water admissions or passing more sodium out of the body through pee.
Why is Sodium Vital?
Sodium is significant for a few capacities within the body. It exists for the most part within the liquid exterior of cells, called extracellular fluid. Its main role is to preserve liquid adjust within the body.
It too plays a key role in controlling the development of materials through cell films, known as cellular transport keeping up the volume of plasma in blood controlling nerve motivations invigorating muscle withdrawals Changes in levels of sodium within the blood can lead to changes in liquid adjust, which can cause a few genuine indications.
Are there Types of Hypernatremia
Hypernatremia reflects a shortfall of add up to body water (TBW) relative to add up to body sodium substance. Since adding up to the body sodium substance is reflected by extracellular liquid (ECF) volume status, hypernatremia must be considered together with the status of the ECF volume:
- Hypovolemia
- Euvolemia
- Hypervolemia
Hypovolemic Hypernatremia
Hypernatremia related to hypovolemia happens with sodium misfortune followed by a moderately more prominent misfortune of water from the body. Common extrarenal causes incorporate most of those that cause hyponatremia and volume consumption.
Renal causes of hypernatremia and volume depletion include treatment with diuretics. Circle diuretics hinder sodium reabsorption within the concentrating parcel of the nephrons and can increment water clearance. Osmotic diuresis can too disable renal concentrating capacity since a hypertonic substance shows within the tubular lumen of the distal nephron. Glycerol, mannitol, and every so often urea can cause osmotic diuresis coming about in hypernatremia. Since glucose does not enter cells within the nonappearance of affront, hyperglycemia assist dehydrates the intracellular liquid (ICF) compartment. The degree of hyperosmolality in hyperglycemia may be clouded by the bringing down of serum sodium coming about from the development of water out of cells into the ECF (translational hyponatremia). Patients with renal illness can moreover be inclined to hypernatremia when their kidneys are incapable of maximally concentrating pee.
Euvolemic Hypernatremia
Hypernatremia with euvolemia may be diminished in TBW with near-normal add-up to body sodium (immaculate water shortage). Extrarenal causes of water misfortune, such as over-the-top sweating, result in a few sodium misfortune, but since sweat is hypotonic (especially when individuals are warmly acclimatized), hypernatremia can result before significant hypovolemia. A shortage of nearly simple water happens in central diabetes insipidus and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
Fundamental hypernatremia (essential hypodipsia) once in a while occurs in children with brain harm and chronically sick more seasoned grown-ups. It is characterized by a disabled thirst instrument (eg, caused by lesions of the brain's thirst center). The modified osmotic trigger for vasopressin discharge is another conceivable cause of euvolemic hypernatremia; a few injuries cause both an impeded thirst component and a changed osmotic trigger. The nonosmotic discharge of vasopressin appears intact, and these patients are by and large euvolemic.
Hypervolemic Hypernatremia
Hypernatremia in uncommon cases is related to volume overload. In this case, hypernatremia comes about from hoisted sodium admissions related to restricted get to the water. One case is the over-the-top organization of hypertonic sodium bicarbonate in the treatment of lactic acidosis. Hypernatremia can moreover be caused by the organization of hypertonic saline or erroneously defined hyperalimentation.
Pathophysiology of Hypernatremia
Sodium is critical to preserve extracellular fluid (ECF) volume. Changes within the ECF volume give input to preserve and add up to sodium substance by expanding or diminishing sodium excretion within the pee. Sodium excretion moreover includes administrative instruments such as the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone frameworks. When serum sodium increments, the plasma osmolality increments which triggers the thirst reaction and ADH emission, driving renal water preservation and concentrated pee.
Hypernatremia Causes and Chance Components
The essential causes of hypernatremia are not sufficient liquid admissions or as well as much misfortune of liquids, driving to inadequate fluid within the blood.
A few well-being components can cause hypernatremia or increment its probability.
These include:
Taking certain drugs or having huge ranges of burned skin can too lead to too much sodium in the blood.
Certain individuals are more likely to create hypernatremia, including:
- Newborn children
- More seasoned grown-ups
- Individuals with a changed mental state
- Individuals accepting IV medicines
- Individuals accept supplements through a tube that runs through the nose and into the stomach, known as nasogastric nourishing
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Hypernatremia?
The major side effect is thirst. The foremost vital signs result from brain cell shrinkage and incorporate perplexity, muscle jerking, or fits. With serious heights, seizures, and comas may occur.
Serious indications are as a rule due to the intense rise of the plasma sodium concentration to over 157 mmol/L[10] (typical blood levels are by and large around 135–145 mmol/L for grown-ups and the elderly). Values over 180 mmol/L are related to a tall mortality rate, especially in adults. In any case, such tall levels of sodium once in a while happen without serious coexisting therapeutic conditions. Serum sodium concentrations have extended from 150 to 228 mmol/L in survivors of intense salt overdosage, whereas levels of 153–255 mmol/L have been watched in fatalities. Vitreous humor is considered to be a distant better; much better; a higher; stronger; an improved; a much better after-death example than after-death serum for evaluating sodium inclusion in a passing.
Evaluation of Hyponatremia
The etiology of hypernatremia as a rule is clear based on history and physical examination. Plasma volume, plasma osmolality, pee volume, concentrating capacity, and osmolality can offer assistance to advance separation between renal and extrarenal causes. In DI, the pee is improperly weakened with ordinary pee volume, and pee osmolality less than the serum osmolality. When DI is suspected, a water hardship test may be performed with the organization of desmopressin. In central DI, desmopressin organization illustrates an increase in pee osmolality, while within the nephrogenic assortment, there's no reaction to desmopressin. In extrarenal causes, the body tries to preserve liquids with fittingly moo pee volume, tall particular gravity, and pee osmolality more noteworthy than serum osmolality.
Hypernatremia Indications
- Having as well as much sodium within the blood may cause no indications, and an individual may be ignorant of it.
- In any case, it can cause indications and complications such as over-the-top thirst weakness perplexity changes in temperament muscle jerking fit seizures coma.
- In most cases, a fundamental well-being condition such as kidney illness or diabetes is behind hypernatremia.
- A specialist may begin the symptomatic preparation by inquiring about a person's therapeutic history and doing a physical examination.
- In case they suspect hypernatremia, they may run blood or pee tests. Both can appear as an expanded nearness of sodium.
How is Hypernatremia Treated?
The foundation of treatment is an organization of free water to rectify the relative water shortfall. Water can be supplanted orally or intravenously. Water alone cannot be managed intravenously (since osmolarity issues drive to the breaking of ruddy blood cells within the circulation system) but maybe can be given intravenously in arrangement with dextrose (sugar) or saline (salt). In any case, excessively quick rectification of hypernatremia is possibly exceptionally unsafe. The body (in specific the brain) adjusts to the higher sodium concentration. Quickly bringing down the sodium concentration with free water, once this adjustment has happened, causes water to stream into brain cells and causes them to swell. This may lead to cerebral edema, possibly coming about in seizures, lasting brain harm, or passing. In this manner, critical hypernatremia ought to be treated carefully by a doctor or other restorative proficient with encounter in the treatment of electrolyte awkwardness. Particular medicines such as thiazide diuretics (e.g., chlorthalidone) in congestive heart disappointment or corticosteroids in nephropathy moreover can be utilized.
Hypernatremia Treatment
All treatment for hypernatremia includes redressing the fluid and sodium adjust within the body. This usually means treating the basic well-being condition.
The leading approach changes, depending on the basic cause. For case, if a person is finding it troublesome to oversee their diabetes, the specialist will prescribe ways to assist.
The Treatment May Include:
- The individual drinking more water
- A healthcare professional regulating IV liquids
- A specialist checks sodium levels and alters the sum of liquids in a like manner.
Can I Prevent Hypernatremia?
Hypernatremia may stem from a diverse well-being issue that requires treatment.
To avoid hypernatremia, an individual can moreover:
- Drink a bounty of water to remain hydrated. Increase their liquid admissions as required, in hot climates or amid physical movement. Have an adjusted, sound slim down.
- Make beyond any doubt other well-being conditions, such as diabetes or kidney illness, well-managed.
- A tall sodium admission does not typically cause hypernatremia unless the admission is intemperate or the individual has certain other fundamental well-being issues.
- Still, a tall sodium count of calories may cause other negative impacts, counting expanded blood weight.









