It is known as esophageal cancer. It is present in the esophagus due to the overgrowth of cells. Cancer occurs in any part of the body due to over multiplication of cells.
Introduction:
It is known as esophageal cancer. It is present in the esophagus due to overgrowth of cells. Cancer occurs in any part of the body due to over multiplication of cells.
Esophagus
Another name is food pipe. It is a hollow, muscular tube that makes the passage between the oral cavity and mouth. There is a common opening for the esophagus and trachea. In front of the trachea also known as the windpipe and behind this spine is present.
Size: the size of the esophagus is 13-14 inches long in adults. Upper esophageal sphincter: It is a special muscular ring that is present at the opening of the upper esophagus. It senses the solid and liquid food and then opens the sphincter through which food passes. When we swallow and the sphincter relaxes it opens the esophagus and food passes and reaches into the stomach through it.
Gastroesophageal (GE) junction: It is the junction that connects the stomach with the lower part of the esophagus. The lower part of the esophagus also contains one specialized muscle ring which is known as the lower esophageal sphincter. When our stomach is empty this sphincter closes thus the juices and acid of the stomach stay away from the esophagus. Esophageal cancer mostly starts in the innermost layer of the mucosa of the esophagus.
Causes:
- Chronic Smokers
- Alcoholic persons
- Acid reflux and Chronic heartburn
- Due to Gastroesophageal reflux distress (GERD) Barnett's esophagus: this occurs due to GERD
- Achalasia occurs in lower part of esophagus
- It can also occur due to some mutation in the DNA of cells present in it which grows abnormally and sometimes also invades other parts of the body. Most commonly it is seen in obese and tobacco chewers patients. Poor food habits
- In patients who undergone radiotherapy
- HPV is also the reason it causes changes in the tissues of vocal cords and oral cavity and on your hands, feet and genitals. In the people who already suffer from cancer of stomach or mouth have high chances to develop cancer of esophagus.
- People who work in chemical factory get more exposed to chemicals like dry cleaning solvents they get ingested and causes irritation in the esophagus which causes esophageal cancer.
Signs and Symptoms
- It can create problem in swallowing (dysphagia)
- Pain while swallowing and eating meat and other hard substances. These tumor can also block the which creates difficulty in liquid intake. liquid intake may be painful to swallow.
- Severe weight loss occurs without any efforts
- Their is burning, pain and heaviness in the chest
- Difficulty in digestion and heartbirn also occurs
- Voice becomes hoarse and cough with sputum
- In early cases of cancer there is no such symptoms
- There is pain in your neck region or back, and sometimes in breastbones and behind it. Pain can also occurs in chest cavity or between the shoulders
- Patient gave a history of recurrent vomiting and sometimes blood also present in the sputum and vomiting.
Complications
- Blockage occurs in esophagus. Bleeding in the esophagus. Esophageal cancer can cause bleedingin the vomiting and sputum. Bleeding is sudden and severe sometimes.
Mainly Two Types of Esophageal Cancer Are:
- Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Esophageal adenocarcinoma
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Squamous cells are the inner lining of esophageal mucosa. When the cancer occurs in the squamous cells of esophagus it is known as squamous cell carcinoma. Location: It can locate anywhere in food pipemostly seen in the neck region (cervical esophagus) and in the upper two-thirds of the chest cavity (upper and middle thoracic esophagus).
Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
When cancer occurs in the glandular cells those cells which make mucus are known as adenocarcinoma.
Location: These are mostly found in the lower third region of the esophagus. In Barrett's esophagus, where there is already irritation present in the esophagus this irritation causes changes in the squamous cells of the esophagus which are in the inner layer of mucosa in the lower part of the esophagus and further causes adenocarcinoma.
Pathophysiology
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma:
The risk factors are smoking and alcohol.
Alcohol and tobacco are combined and they show synergistic effects which causes increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus.esophageal epithelium has the ability to dissolve fat compounds the same capability is present in alcohol. Aromatic amines, nitrosamines and polycyclic hydrocarbons are tobacco carcinogens because of this they have the ability to cross the epithelium deeply of the esophagus and the alcohol promotes this.
DNA of epithelial cells are destroyed by alcohol which decreases the capacity of metabolism of epithelial cells. Because of this the cells are not capable of living and are not able to protect themselves from oxidation. Inflammation occurs in the squamous epithelium due to oxidation. Continuous irritation of the epithelium leads to dysplasia and malignant transformation.
Esophageal adenocarcinoma:
The risk factors are gastroesophageal reflux disease and obesity.
The chronic reflux of gastric acid and bile at the gastroesophageal junction The irritation of squamous epithelium which lines the esophagus occurs due to chronic reflux of bile and gastric acid. Metaplasia of esophagus occurs due to irritation. The lining of the esophagus changes from non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium to columnar epithelium by the gastro esophageal reflux distress. This condition is known as Barrett's esophagus .
The progression of Barrett's esophagus to adenocarcinoma is associated with changes in genetic and protein structure, as well as gene expression.
Mutations include:
- Chromosome no. Losses (4q, 5q, 9p) Chromosome no. gains (8qand 20q)
- Gene amplifications occur in (7, 8, and 17q)
- PT53 genes and P16 genes
- Variants in ADH and/or ALDH2 genes
In addition, overweight is implicated in the development of esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Patients with overweight tend to have hypertrophic adipocytes and inflammatory cells within their fat deposits.
This forms a microenvironment within the adipocyte that promotes tumor development through the release of cytokines.
Adipocytes potentiate tumor expansion by supplying energy to support the tumor's growth.
Pathology
Squamous cell carcinoma or adenocarcinoma of the esophagus may look like:
- Flat and irregular plaque.
- Looks polypoid
- Ulcerated mass, fungating mass.
Location
Squamous cell carcinoma is usually seen in the middle third of the esophagus.
Adenocarcinoma is seen in the lower region of the esophagus near the gastric opening.
Diagnosis
The following tests used to diagnose esophageal cancer include:
Barium swallow study
In this test, a solution of barium has to be drunk which helps in the vision of cancerous cells and then undergo X-rays. The barium lines the inner lining of the esophagus, which then shows any changes that occur in the tissue of the esophagus on the X-ray.
Endoscopy
During this procedure, a surgeon passes a flexible tube equipped with a video lens (video endoscope) which is passed your throat and into your esophagus. Using the endoscope, the doctor examines the tissues of the esophagus and looks for any cancer or areas of irritation.
Biopsy
Physicians may use a special scope which is passed down your throat into your esophagus to collect a sample of tissue that is irritated. The tissue sample is then checked in a laboratory for cancer cells.
Additional Tests Include:
- Bronchoscopy
- Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
- Computerized tomography (CT)
- Positron emission tomography (PET)
- Chest X-ray.
Bronchoscopy - The trachea and airways are checked with a bronchoscope, a thin tube that is inserted through the nose or mouth.
CT scan - A procedure that forms sharp images of the inside portion of the body.
Endoscopic ultrasound - Used during endoscopy, a particular amount of sound waves with particular frequency hits and passes organs in the body to create images called sonograms.
Thoracoscopy - An endoscope is inserted into the chest cavity through an incision to check the inside of the chest to look for lymph nodes and other chest organs that may have cancer. Biopsies can be done additionally for confirmation.
Laparoscopy - The lighted tube is passed through an incision in the abdomen to examine the abdominal organs and take tissue of esophagus to check for cancer.
Prevention
Following things should be done to reduce the risk of esophageal cancer:
- Quit smoking. If you are a heavy smoker, talk to your doctor about quitting this bad habit.
- Medications and counseling for awareness are available which help you quit.
- Don't start tobacco under any kind of influence from others.
- Drink alcohol in less amounts, so that it will cause less harm to your body and also if you are not able to quit.
- For healthy adults, it is necessary to drink one drink a day for women and two drinks a day for men.
- Eat more healthy things like fruits and green vegetables. Add a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables to your diet that are necessary for your health.
- Maintain good health and moderate weight. If you are overweight or obese, try to reduce your weight with exercise and a good diet plan. You have to motivate yourself for a slow and steady weight loss.
- In esophageal cancer it is diagnosed by injecting a dye that is seen in ultrasonography also.
Treatment
If the cancer has been detected in an early stage, surgical treatment with a conservative intention may be possible. Small tumors that only involve the mucosa or lining of the esophagus may be removed by endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR). Otherwise, curative treatment of early-stage disease may entail removal of the whole or part of the esophagus (esophagectomy), although this is a hard surgery with a relatively high risk of mortality or postoperative complications. The benefits of surgery are less evident in early-stage ESCC as compared to EAC.
Chemotherapy: In this specialized chemicals or drugs are used for the treatment of cancer. The drugs were given before (nonadjuvent) and after the surgery for the treatment of esophageal cancer. Radiation therapy is also used in conjunction with chemotherapy. In patients which have tumor metastasis means tumor invades other tissues in those only chemotherapy is used to relieve the symptoms of cancer. Side effects of chemotherapy are based on the drugs which we used.
Radiation therapy: In this therapy we used high energy beams such as protons and X rays to destroy cells which cause cancer.
External beam radiation: This radiation comes from the machine which is present in the surroundings and this machine shoots rays that are aimed at the cancer cells.
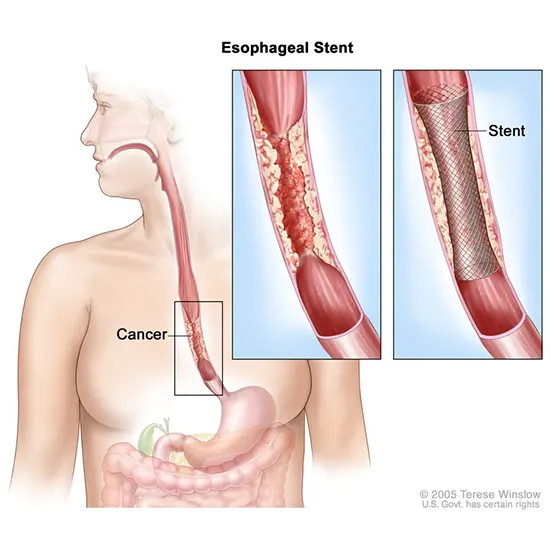
Brachytherapy: In this radiation are inside the body near the site of cancerous tissue. It is also used before or after the surgery for the full relief of symptoms of cancer. This therapy is used in advanced cases of esophageal cancer in which cancer spreads to other tissues and sometimes this cancer causes full blockage of esophagus so that there is difficulty in passing the food to the stomach. Side effects of radiation therapy are: Damage to organs like lungs and heart Sunburn like skin reactions Swallowing becomes difficult
Immunotherapy: In this those drugs are given which boost the immune system of the body for fight with the cancer cells. Cancer cells produce similar proteins like the proteins secreted by normal cells which makes it hard for the immune system to recognize the cancerous cells that are dangerous for our body.
If it is not treated timely it can spread into other organs and can also destroy the organs sometimes it spreads into intestine and if it is not treated the intestine should be dissected. If the small intestine is smaller than 1 meter it causes major problem in digestion due to less peristaltic movements.
Prognosis
Poor prognosis- Because this disease has no early symptoms which are seen in the early stage of the disease which is not helpful in the diagnosis of the disease. The disease is diagnosed at late stages by which time has passed and it is difficult to completely cure the patient. The very first symptom is difficulty in swallowing which is seen in the advanced stages. After the patient is diagnosed with esophageal cancer at an advanced stage the life expectancy of the patient is only 5 years. If the carcinoma is only in the mucosal region of the esophagus the life expectancy is 5 years but if it invades the submucosa also the life expectancy will reduce.









