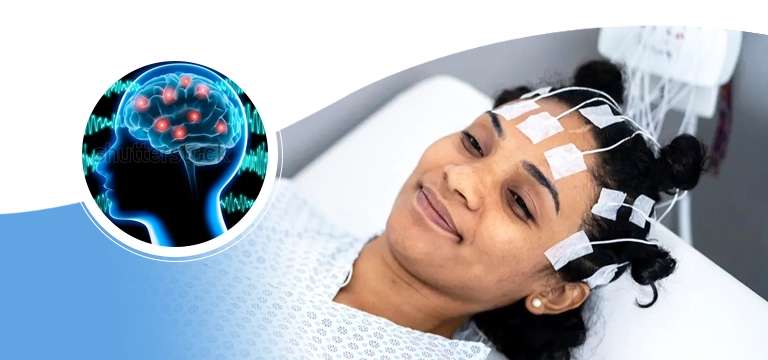
An electroencephalogram (EEG) test is a diagnostic procedure used to measure and record the electrical activity of the brain. It is a non-invasive technique that helps doctors evaluate and diagnose various neurological...
What is EEG test?
An electroencephalogram (EEG) test is a diagnostic procedure used to measure and record the electrical activity of the brain. It is a non-invasive technique that helps doctors evaluate and diagnose various neurological conditions and disorders. The EEG test provides valuable information about the brain's functioning and can aid in the assessment of seizures, sleep disorders, brain injuries, and other neurological abnormalities.
Why EEG Test is done?
EEG tests are conducted for various reasons to evaluate and diagnose neurological conditions and disorders. Here are some common reasons why an EEG test may be done:
- Seizure disorders: EEG is used to diagnose & monitor epilepsy and other seizure disorders. It helps identify abnormal electrical activity in the brain that may be causing seizures.
- Sleep disorders: EEG is used to study brain activity during sleep, helping diagnose sleep disorders such as sleep apnea, narcolepsy, and parasomnias.
- Altered consciousness: EEG can assess brain function in cases of altered mental states, coma, or unexplained periods of unconsciousness.
- Brain injuries: EEG is employed to evaluate brain function following head trauma, such as concussions or brain hemorrhages. It helps determine the extent of brain damage and monitor recovery.
- Brain tumors: EEG can assist in locating the region of the brain affected by a tumor and assess the impact of the tumor on brain activity.
- Stroke assessment: EEG may be used to evaluate brain activity in cases of stroke or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) to determine the extent of damage.
- Evaluation of cognitive disorders: EEG can be helpful in assessing cognitive disorders like dementia, Alzheimer's disease, or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
- Evaluation of unexplained symptoms: If a patient experience fainting, dizziness, EEG can help identify any abnormal brain activity associated with these symptoms.
- Monitoring brain function during surgery: During any surgery, EEG is to ensure the brain is functioning normally and it also helps to detect any potential complications.
Conditions Diagnosed by EEG?
Some of the conditions that can be diagnosed or assessed with an EEG include:
- Psychiatric disorders: Sometimes in psychiatric evaluations to identify abnormal brain activity with certain mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety disorders, and schizophrenia EEG is often used.
- Encephalopathy: EEG helps diagnose and monitor encephalopathy, which is a condition characterized by brain dysfunction due to infections.
- Epilepsy and seizure disorders: EEG is crucial in diagnosing and monitoring epilepsy. It helps identify abnormal electrical activity in the brain that is associated with seizures.
- Brain tumors: EEG can aid in the evaluation of brain tumors by identifying abnormal electrical patterns and locating the affected area in the brain.
- Brain injuries: EEG is used to assess brain function following traumatic brain injuries, it helps determine the extent of damage and monitor recovery.
- Stroke: EEG may be utilized to assess brain function and detect abnormalities associated with strokes or TIAs.
- Neurological disorders: EEG can aid in the evaluation of various neurological disorders, including, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, and Huntington's disease.
- Disorders: EEG may be used in the diagnosis and assessment of developmental disorders and cognitive disorders.
What are the EEG Procedures and Preparations?
- Procedure: The EEG (electroencephalogram) procedure involves several steps to accurately measure and record the electrical activity of the brain. Here is an overview of the typical EEG procedure:
- Precautions: Before EEG, the patient is advised to follow certain instructions, and It's important to inform the healthcare provider about any ongoing medications.
- Electrode Placement: The patient is positioned comfortably, either sitting or lying down. The technician then measures and mark’s specific locations on the scalp using a specialized pre-marked cap tool.
- Skin Preparation: The areas on the scalp where the electrodes will be attached are cleaned using an abrasive gel to remove any oil, dead skin, or debris that could interfere with the electrode.
- Electrode Application: The electrodes are attached to the prepared scalp areas using a conductive adhesive gel. The electrodes are typically held in place using gentle pressure or an elastic cap.
- Recording Session: Once the electrodes are securely in place, the EEG recording session begins. The patient is asked to remain as still as possible during the procedure to minimize artifacts in the recorded brain activity.
- Monitoring and Observation: The neurologist monitors the recording session to ensure the quality of the EEG signals and to make note of any significant events.
- Additional Stimuli: Specific stimuli may be employed to trigger certain brain responses, like breathing exercises or flashing lights.
- Recording Duration: In most cases, a standard EEG recording session lasts between 20 minutes to one hour.
- Electrode Removal: After the session, the electrodes are carefully removed from the scalp. Any residual adhesive is typically wiped off, & patient is allowed to wash their hair.
- Interpretation and Reporting: The recorded EEG data is analyzed and interpreted by a neurologist. They review the brain wave patterns to provide a detailed report. The report is then shared with the referring healthcare provider, who will discuss the findings with the patient and recommend further steps.
- Preparations: To ensure accurate and reliable results during an EEG (electroencephalogram) test, here are some common EEG preparations for it:
- Medication instructions: Inform the healthcare provider about any medications one is currently taking. They will provide specific instructions regarding whether one need to continue or discontinue any medications that could affect brain activity.
- Hair care: It is generally recommended to arrive with clean, dry hair on the day of the EEG. Avoid using any kind of hair products that may interfere with electrode adhesion or cause artifacts in the recordings.
- Caffeine and food restrictions: Avoid caffeine for a certain period before the EEG test, since it can affect brain activity.
- Sleep deprivation: This is required to capture specific brain activity patterns. The healthcare provider will inform the patient if they need to limit sleep before the EEG.
- Clothing: Wearing comfortable and loose-fitting clothing to the EEG appointment is necessary. Some facilities may provide a gown or provide specific instructions on what to wear.
- Avoidance of electronic devices: Patient may be instructed to avoid use of electronic devices like smartphones, smart watches etc., since they emit electromagnetic waves which can potentially interfere with the EEG recording.
What is the Test price of EEG?
It's always advisable to contact specific healthcare providers, diagnostic centers, to inquire about the cost of an EEG test, as prices may differ depending on the location & facility, however, cost of a basic EEG test in India can range from approximately ₹2000 to ₹5,000.
Best Diagnostic Center for EEG Test?
The one of best diagnostic center for EEG is Ganesh Diagnostic & Imaging Centre, which is known for their exceptional neurology services. With a team of highly skilled neurologists and technicians, they offer cutting-edge EEG technology and state-of-the-art facilities. Patients at Ganesh Diagnostic & Imaging Centre can expect a seamless experience from start to finish, with meticulous electrode placement, comfortable testing environments, and accurate data recording. The center prioritizes patient comfort and convenience, ensuring that individuals feel at ease during the procedure. The EEG results are interpreted by experienced neurologists who provide detailed and comprehensive reports to aid in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.









