Book Antigen For Plasmodium Falciparum Appointment Online Near me at the best price in Delhi/NCR from Ganesh Diagnostic. NABL & NABH Accredited Diagnostic centre and Pathology lab in Delhi offering a wide range of Radiology & Pathology tests. Get Free Ambulance & Free Home Sample collection. 24X7 Hour Open. Call Now at 011-47-444-444 to Book your Antigen For Plasmodium Falciparum at 50% Discount.
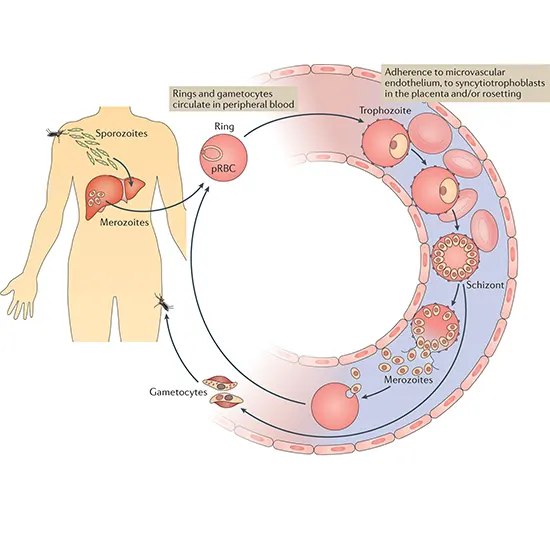
Falciparum malaria. The trophozoite and immature gametocyte stages produce and release the HRP-II antigen, which is persistent in peripheral blood. Consequently, following chemotherapy and parasite clearance, HRP-II tests can stay positive for up to 2 weeks, as shown by microscopy.
The unicellular protozoan parasite Plasmodium falciparum is responsible for the most dangerous type of malaria in humans.
P. falciparum predominates in Africa but is present worldwide in tropical and subtropical regions. Because P. falciparum multiplies quickly in the blood, it can induce considerable blood loss and cause severe malaria (anemia).
The cytoplasm of P. falciparum rings is fragile, with one or two tiny chromatin spots.
Malaria antigens are found in the blood sample by the malarial falciparum and vivax antigen test. A species of the parasite Plasmodium is the cause of the infection.
We discovered that, along with IgG, merozoite-specific IgM is significant during malaria in children and adults with lifetime exposure and emerges quickly during Plasmodium falciparum infection.
RDTs provide an alternative to clinical diagnosis or microscopy, particularly in situations where high-quality microscopy services are challenging.
Children infected with P. falciparum are likely to develop severe anemia due to additional hemolysis of noninfected RBCs by host immunity.
The parasite Plasmodium falciparum that causes human malaria has the greatest fatality rate. The ability of this species to obstruct the host's physiological functions while it is still developing is what gives it its exceptional virulence.
The reason P. falciparum is more virulent than other human malaria parasites is that parasites can infect different stages of red blood cells, which results in a higher parasite biomass.
The number of genes in Plasmodium falciparum.
5,300 genes
Here, we provide findings from an investigation of P. falciparum clone 3D7's genomic sequence. The most (A + T)-rich genome to date, the 23-megabase nuclear genome is made up of 14 chromosomes and around 5,300 genes.
Blood testing may reveal: The parasite's presence in your blood is proof that you have malaria.
| Test Type | Antigen For Plasmodium Falciparum |
| Includes | Antigen for Plasmodium Falciparum (Pathology Test) |
| Preparation | |
| Reporting | Within 24 hours* |
| Test Price |
₹ 400
|

Early check ups are always better than delayed ones. Safety, precaution & care is depicted from the several health checkups. Here, we present simple & comprehensive health packages for any kind of testing to ensure the early prescribed treatment to safeguard your health.