The CT (Computerised Tomography) scan is crucial for monitoring a variety of medical disorders. It is a useful diagnostic tool for tracking the development of diseases and assessing the efficacy of therapies due to its...
The CT (Computerised Tomography) scan is crucial for monitoring a variety of medical disorders. It is a useful diagnostic tool for tracking the development of diseases and assessing the efficacy of therapies due to its capacity to provide detailed cross-sectional images of various body areas. Following are a few instances of how CT can be applied in follow-up:
Cancer Follow-up
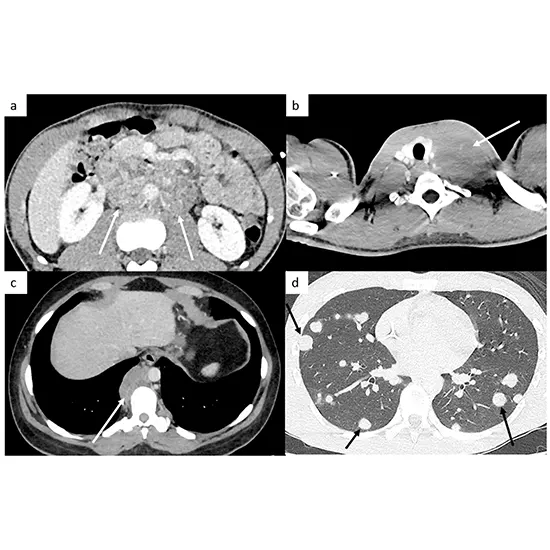
CT (computed tomography) imaging is essential for providing cancer patients with ongoing care. Patients often have routine CT scans after receiving a cancer diagnosis and treatment to check for any potential cancer recurrence or disease progression.
The following are the important points about CT's function in cancer follow-up care:
To check for probable cancer development or recurrence, cancer patients receiving follow-up care may have CT imaging.
Doctors can spot any changes in tumors or other tissues because of the precise images of the body's internal components that CT scans reveal.
The size, shape, position, and characteristics of any tumors or lesions present can be learned via CT scans, which also can detect tumors that are too small to be felt during a physical examination.
To give a more complete view of the malignancy and its course, CT scans may be utilized in conjunction with other imaging studies, like PET scans.
By demonstrating whether tumors have decreased or grown in response to treatment, CT scans can be used to evaluate the efficacy of cancer treatment.
CT scans, however, are subject to scheduled radiation, which over time may raise the risk of developing cancer.
Therefore, based on each patient's unique requirements and medical background, the frequency and schedule of CT scans should be carefully assessed.
Trauma follow-up
CT (computed tomography) imaging can be used to diagnose injuries, evaluate the efficacy of treatment, and keep track of potential problems in trauma patients who need follow-up care. The following are some key characteristics of CT in trauma follow-up:
Injury detection
By providing precise images of the body's internal components, CT scans enable medical professionals to identify injuries that might not be apparent on other imaging tests, including X-rays or MRIs. Fractures, internal bleeding, organ damage, and other soft tissue injuries are examples of this.
Treatment effectiveness
CT scans can be used to monitor the development of healing and evaluate the efficacy of treatments, including surgical procedures and non-surgical therapy.
Monitoring for complications
CT scans can also be used to keep an eye out for problems like infections, blood clots, or other injuries that might not have been noticed right away after trauma, such as those.
Rapid diagnosis
CT scans are a useful tool in emergencies where time is of the essence because they may be completed fast. They can support doctors in developing a treatment strategy and quickly identifying injuries.
Minimally invasive
CT scans are non-invasive, which means that no incisions or other intrusive procedures are necessary. In addition to lessening the patient's suffering, this can help lower the chance of problems.
Radiation exposure
Patients who undergo CT scans are subjected to ionizing radiation, which over time may raise their chance of developing cancer. When it comes to trauma follow-up, the advantages of CT imaging often outweigh the hazards, particularly in emergency cases where quick diagnosis is crucial.
Overall, CT imaging is a useful tool in the post-trauma care of patients, enabling medical professionals to identify injuries, evaluate the efficacy of treatment, and keep an eye out for any potential problems.
Postoperative Follow up
A surgical procedure's success can be determined and any post-operative issues can be found with the use of CT (computed tomography) imaging in post-operative follow-up treatment. The following are some key CT post-operative follow-up characteristics:
Assessing surgical access
CT scans can be used to determine whether the planned outcome has been attained while evaluating the success of surgical treatment. This may involve determining how much of the tumor has been removed or how damaged tissues or organs will be rebuilt.
Finding post-operative complications
CT scans are useful for finding complications following surgery, such as fluid accumulations, abscesses, or infections. Other imaging techniques, such as -rays or physical exams, could not show these issues.
Tracking Healing
CT scans can be used to track the recovery from surgery, enabling medical professionals to gauge how well the wound is healing or whether any complications have disappeared.
Planning additional therapy
CT scans can assist in directing additional treatment plans, such as figuring out whether more surgery or other procedures are required.
Minimally invasive
CT scans are non-invasive, which means that no incisions or other intrusive procedures are necessary. In addition to lessening the patient's suffering, this can help lower the chance of problems.
Radiation exposure
Patients who undergo CT scans are subjected to ionizing radiation, which over time may raise their chance of developing cancer. However, when used carefully, the advantages of CT imaging for post-operative follow-up typically outweigh the risks.
Overall, CT imaging is a valuable tool in post-operative follow-up care, allowing doctors to assess surgical success, detect complications, monitor healing, and plan further treatment as needed.
Disease follow-up
The type and stage of the disease determine the role of CT in a disease's follow-up:
Heart disease Patients
CT scans can be used on heart disease patients to track the disease's development and evaluate the efficacy of treatment. A specific form of CT scan called angiography can offer precise pictures of the heart and blood vessels, enabling medical professionals to look for blockages or other problems that could need treatment.
Lung disease patients
CT scans may be used on patients with lung disease to track the disease's development and evaluate the efficacy of treatment. With the help of CT scans, clinicians may identify changes in lung tissue and evaluate the efficacy of treatment by viewing precise images of the lungs.
Overall, CT imaging is crucial for follow-up care because it enables medical professionals to track the development of a patient's condition, evaluate the effectiveness of their therapy, identify any complications, and direct additional care as necessary.









