
A tumor of brain is an abnormal growth of brain cells. The brain tumor can be cancerous or non-cancerous. Brain tumors can develop in any part of the brain and can cause a range of symptoms, including headaches,...
A tumor of brain is an abnormal growth of brain cells. The brain tumor can be cancerous or non-cancerous. Brain tumors can develop in any part of the brain and can cause a range of symptoms, including headaches, seizures, vision problems, and changes in behavior or personality. Some risk factors have been identified, including exposure to radiation, a family history of brain tumors, and certain genetic conditions. The treatment of brain tumor depends on the type and spread of brain tumor.
Types of brain tumor
The brain tumor is of many different types and they are generally classified based on the type of cells they arise from, their location in the brain, and whether they are malignant or benign.
Some common types
Gliomas : These tumors arise from glial cells, which support and nourish the neurons in the brain. Gliomas account for 30% of all brain tumors. These tumors can be benign or malignant. The most common types of gliomas include astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and ependymomas.
Meningiomas : These tumors arise from the meninges. Meninges are the thin layers of tissue that cover the brain and spinal cord. Meningiomas are usually benign and grow slowly, but they can cause symptoms if they compress nearby brain tissue.
Pituitary adenomas : These are tumors arise from the pituitary gland. Pituitary adenomas can cause hormonal imbalances and may require treatment with medication, radiation, or surgery.
Medulloblastomas : These malignant tumors arise in the cerebellum(the part of the brain). The cerebellum controls movement and coordination. This tumor is common in children than adults, and they can cause symptoms such as headaches, nausea, and difficulty with balance and coordination.
Schwannomas : These are tumors that arise from the cells that form the myelin sheath around nerves. Schwannomas can occur in the brain or spinal cord and are usually benign, but they can cause symptoms if they compress nearby nerves.
There are many other types of brain tumors, and each type may have its own unique characteristics and treatment options.
Stages of brain tumor
Brain tumors are generally classified into different stages based on their size, location, and how far they have spread. The most common staging system used for brain tumors is the TNM system, which stands for Tumor, Nodes, and Metastasis.
Here are the stages of brain tumors
Stage 0 : This stage of brain tumors that have not spread beyond the original site of the tumor and are still in the early stage of tumor development.
Stage I : The stage refers to small-size tumors that are localized and have not spread to any nearby tissue.
Stage II : This stage refers to tumors that are larger and have started to invade nearby tissues, but have not yet spread to distant parts of the brain.
Stage III : This stage refers to tumors that have invaded nearby tissues and are starting to spread to distant parts of the brain.
Stage IV : This stage refers to tumors that have spread to distant parts of the brain or other parts of the body.
The staging of brain tumors is important because it helps doctors determine the appropriate treatment options and predict the outcome of the disease. The stage of the tumor can also affect the patient's quality of life and overall prognosis. However, it's important to note that each patient's situation is unique, and treatment decisions should be made on an individual basis.
Symptoms of Brain Tumors
The symptoms of a brain tumor can vary depending on the location and size of the tumor as well as how quickly it is growing.
The most common brain tumor symptoms are:
Headaches : Persistent headaches, especially ones that get worse over time, are a very common symptom of a brain tumor. They may be more severe in the morning or while lying down.
Seizures : Seizures are another common symptom of a tumor of the brain. They can range from mild to severe and may cause the patient to lose consciousness or experience convulsions.
Vision Problems : A brain tumor can affect vision in various ways, including blurred vision, double vision, or loss of peripheral vision.
Weakness or numbness : A brain tumor can cause numbness or weakness in one part or side of the body.
Behavioural or personality Change : A brain tumor can cause changes in behavior, mood, or personality, such as increased irritability, depression, or confusion.
Speech problems : A brain tumor can cause difficulty speaking or understanding language.
Loss of balance or coordination : A brain tumor can affect the part of the brain that controls balance and coordination, leading to difficulty walking or standing.
Nausea and vomiting : A brain tumor can cause nausea and vomiting, especially in the morning.
Causes of Brain Tumor
There are various different factors that are thought to contribute to the development of brain tumors. Some most common causes of brain tumors:
Genetic Factors : Some genetic conditions such as neurofibromatosis and Li-Fraumeni syndrome, increase the risk of developing tumors of the brain.
Exposure to harmful radiation : Exposure to high levels of radiations be it from any medical treatment or any environmental source, is a known risk factor for brain tumors.
Age : Compare to others, Brain tumors are common in older adults, although they can occur at any age.
Family history : Having a family history of brain tumors or other types of cancer may increase the risk of developing a brain tumor.
Immune system disorders : Some immune system disorders, such as HIV/AIDS, may increase the risk of developing a brain tumor.
Chemical exposure : Exposure to certain chemicals, such as pesticides or industrial chemicals, may increase the risk of developing a brain tumor.
Head injuries : Severe head injuries, especially those that cause bleeding in the brain, may increase the risk of developing a brain tumor later in life.
Risk factors of brain tumor
Several risk factors that increase a person's likelihood of developing a brain tumor.
Some common risk factors of brain tumor are
Age : The tumors of brain are common in older adults, although this can occur in the individual of any age group.
Gender : Some types of brain tumors, such as meningiomas, are more common in women, while others, such as gliomas, are more common in men.
Genetics : Some genetic conditions, such as neurofibromatosis and Li-Fraumeni syndrome, increase the risk of developing brain tumors.
Exposure to radiation : Exposure to high levels of radiation, either from medical treatments or environmental sources, is a known risk factor for brain tumors.
Family history : Having a family history of brain tumors or other types of cancer may increase the risk of developing a brain tumor.
Immune system disorders: Some immune system disorders, such as HIV/AIDS, may increase the risk of developing a brain tumor.
Chemical exposure : Exposure to certain chemicals, such as pesticides or industrial chemicals, may increase the risk of developing a brain tumor.
Head injuries : Severe head injuries, especially those that cause bleeding in the brain, may increase the risk of developing a brain tumor later in life.
Prevention of brain tumor
There is no surefire way to prevent brain tumors, but there are some steps you can take to reduce your risk.
Some tips for preventing brain tumors
Protect your head : Wearing a helmet when participating in activities that could result in a head injury, such as biking, skating, or playing contact sports, can help reduce your risk of developing a brain tumor.
Avoid exposure to radiation : Minimizing your exposure to radiation, both from medical procedures and environmental sources, may help reduce your risk of developing a brain tumor.
Eat a healthy diet : Eating a balanced diet that is high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and low in processed foods and red meat, may help reduce your risk of developing a brain tumor.
Exercise regularly : Regular physical activity has been linked to a reduced risk of developing certain types of cancer, including brain tumors.
Avoid exposure to chemicals : Reducing your exposure to chemicals, such as pesticides and industrial chemicals, may help reduce your risk of developing a brain tumor.
Get regular check-ups : Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help catch any health problems early, including brain tumors.
It's important to note that these steps may not completely eliminate your risk of developing a brain tumor, but they may help reduce your risk. If you are concerned about your risk of developing a brain tumor, talk to your healthcare provider.
Diagnosis of brain tumor
If a brain tumor is suspected, a healthcare provider will typically perform a series of tests to diagnose it. Here are some of the most common diagnostic tests for brain tumors:
Neurological exam : A neurological exam such as EEG, involves evaluating a person's vision, hearing, balance, coordination, and reflexes to look for signs of a brain tumor.
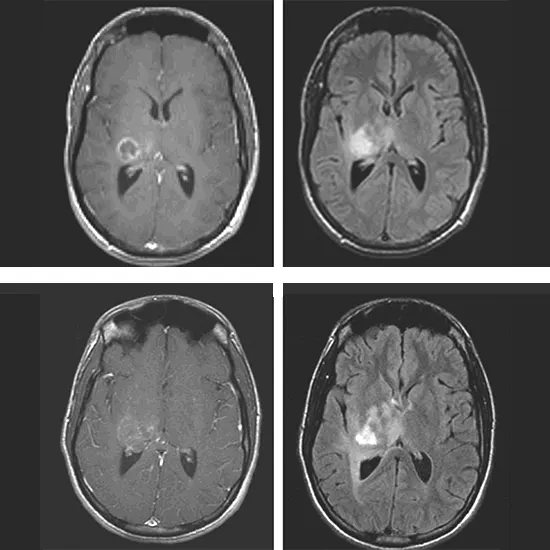
Imaging tests : Imaging tests, such as Skull X-rays, CECT Brain scans, MRI Spectroscopy, and MRI Brain scans, can produce detailed pictures of the brain to help identify any abnormal growths.
Biopsy : A biopsy involves removing a tissue sample from the brain for microscopic examination to determine if it is cancerous.
Blood tests : Blood tests such as complete hemogram, LFT, and KFT can help identify any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the brain tumor.
Spinal tap : A spinal tap involves removing a sample of cerebrospinal fluid, which surrounds the brain and spinal cord, to look for signs of a brain tumor.
Once a diagnosis has been made, the healthcare provider will determine the type and stage of the tumor with MRI Brain tumor protocol, Brain PET scan to guide treatment options.
Conclusion
Brain tumors occur when there are abnormal cell growths in the brain. the growth of cells can be noncancerous or cancerous. It can be checked with the help of various diagnostic procedures. They can be primary, meaning they originate in the brain, or secondary, meaning they have spread from other parts of the body. If you suspect that you or a loved one may have a brain tumor, it's important to seek medical attention promptly to receive a proper diagnosis and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
The detection of Brain Tumors at their initial stage is crucial for treating and maintaining the quality of life. To help a patient who is at high risk of brain tumor development, Ganesh Diagnostic, and Imaging Centre offers Brain Tumor Screening Package. For any queries, contact our expert healthcare executives.















